Site layout plan for construction
Contents |
[edit] What are site layout plans?
Site layout plans are prepared by contractors as part of their mobilisation activities before work on site commences.
These are a crucial part of construction management, as sites can be very complex places involving the co-ordination and movement of large quantities of materials as well as high-value products, plant and people. Effectively and accurately laying out a site can help ensure that the works are undertaken efficiently and safely. Careful sizing and positioning of site facilities can help reduce travel times, congestion, waiting times, and so on, and help to make the site a more effective workplace with better worker morale.
[edit] How is a site layout plan prepared?
Site layout planning involves four basic processes:
- Identifying the site facilities that will be required.
- Determining the sizes, and other constraints for those facilities (such as access requirements, security, services and so on).
- Establishing the inter-relationships between those facilities.
- Optimising the layout of the facilities on the site.
As sites will change in nature during the course of the works, there may be a number of different site layout plans for different phases, and there may be more detailed plans showing particularly complex areas or sequences or describing specific functions.
The use of building information modelling (BIM) can help describe the construction site in three dimensions and through different phases, effectively creating a virtual construction model.
[edit] What should a site layout plan include?
Site layout plans might include locations for and sizes of:
- Zones for particular activities.
- Cranes (including radii and capacities).
- Site offices.
- Welfare facilities.
- Off-loading, temporary storage and storage areas (laydown areas).
- Sub-contractor facilities.
- Car parking.
- Emergency routes and muster points.
- Access, entrances, security and access controls, temporary roads and separate pedestrian routes.
- Vehicle wheel washing facilities.
- Waste management and recycling areas.
- Site hoardings and existing boundaries.
- Protection for trees, existing buildings, neighbouring buildings, and so on.
- Signage.
- Temporary services (including electrical power, lighting, water distribution, drainage, information and communications technology, site security systems, and so on)
- Temporary works (such as propping solutions for retained structures, sheet piling details, and so on).
- Areas for the construction of mock-ups for testing.
- Fabrication facilities.
[edit] Why is a site layout plan necessary?
Problems caused by poor site layout planning can include:
- Inappropriate storage which can result in damage to products and materials.
- Poor siting of plant.
- Poor siting of welfare facilities.
- Inadequate space provision.
- Unsatisfactory access.
- Security and safety issues.
- Poor way finding (due to complex layouts or inadequate signage).
- Demoralised workers, delays and increased costs.
See also: Contractor's site layout planning and Virtual construction model.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Construction phase plan.
- Construction strategy.
- Contractor's site layout planning.
- Haul road.
- Lay down area.
- Lighting of construction sites.
- Main construction compound.
- Mobilisation to site: a quality perspective.
- Pre-construction information.
- Safety signs.
- Site area,
- Site facilities.
- Site office.
- Site plan.
- Site storage.
- Temporary site services.
- Temporary works.
- Virtual construction model.
- Welfare facilities.
- Wheel washing system.
Featured articles and news
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
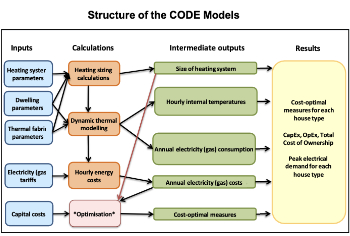
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.