Pediment
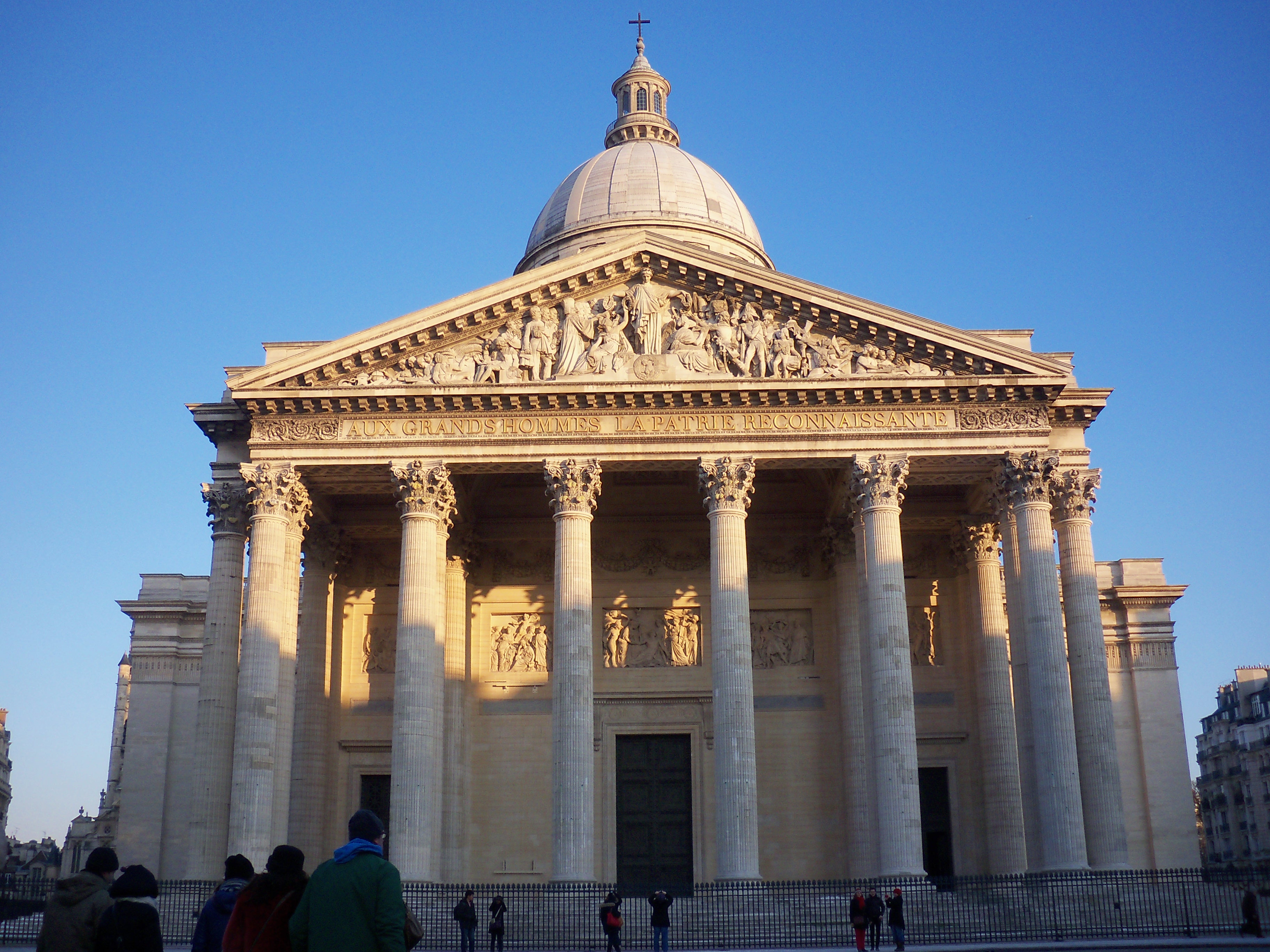
In classical, neoclassical and baroque architecture, a pediment is the triangular gable that forms the end of a pitched roof. It is placed above the horizontal entablature which is typically supported by columns. It is also sometimes seen as the top element of a portico.
In classical Greek temples, the pediment was the crowning feature of the front elevation, with the tympanum (the area within the pediment) being decorated with relief sculptures depicting mythological figures and scenes.
The Romans later adapted the pediment as a decorative finish for doors, windows and niches.
There are a number of variations of the traditional pediment:
- The segmental or arch form in which the angular slopes of the cornice are replaced by a circle segment.
- The broken pediment in which the raking cornice is left open at the apex.
- The open pediment in Georgian architecture, in which the pediment is open along the base.
- The ‘swan-necked pediment’, where the raking cornice takes the form of two S-shaped brackets facing one another.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Acroterion.
- Architectural styles.
- Architrave.
- Barrel vault.
- Bas-relief.
- Broken pediment.
- Classical orders in architecture.
- Cornice.
- Cornice coving and architrave definitions.
- Elements of classical columns.
- Entablature.
- Flying buttress.
- Frieze.
- Gable.
- Moulding.
- Pedestal.
- Pendentive dome.
- Pilaster.
- Pinnacle.
- Soffit.
- Trompe l’oeil.
- Tympanum.
[edit] External references
IHBC NewsBlog
Heritage Building Retrofit Toolkit developed by City of London and Purcell
The toolkit is designed to provide clear and actionable guidance for owners, occupiers and caretakers of historic and listed buildings.
70 countries sign Declaration de Chaillot at Buildings & Climate Global Forum
The declaration is a foundational document enabling progress towards a ‘rapid, fair, and effective transition of the buildings sector’
Bookings open for IHBC Annual School 12-15 June 2024
Theme: Place and Building Care - Finance, Policy and People in Conservation Practice
Rare Sliding Canal Bridge in the UK gets a Major Update
A moveable rail bridge over the Stainforth and Keadby Canal in the Midlands in England has been completely overhauled.
'Restoration and Renewal: Developing the strategic case' Published
The House of Commons Library has published the research briefing, outlining the different options for the Palace of Westminster.
Brum’s Broad Street skyscraper plans approved with unusual rule for residents
A report by a council officer says that the development would provide for a mix of accommodation in a ‘high quality, secure environment...
English Housing Survey 2022 to 2023
Initial findings from the English Housing Survey 2022 to 2023 have been published.
Audit Wales research report: Sustainable development?
A new report from Audit Wales examines how Welsh Councils are supporting repurposing and regeneration of vacant properties and brownfield sites.
New Guidance Launched on ‘Understanding Special Historic Interest in Listing’
Historic England (HE) has published this guidance to help people better understand special historic interest, one of the two main criteria used to decide whether a building can be listed or not.
"Conservation Professional Practice Principles" to be updated by IHBC, HTVF, CV
IHBC, HTVF, and CV look to renew this cross-sector statement on practice principles for specialists working in built and historic environment conservation roles.