Public sewer
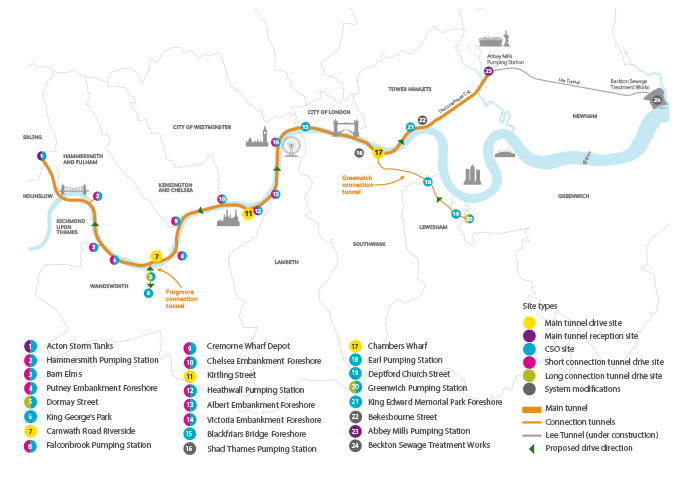
|
| The Thames tideway tunnel comprises a 24km long 7.2m diameter sewer running from Acton in the west to Abbey Mills in the east. It will have a holding storage capacity of 1.6 million cubic metres. |
A pipe that serves only one property is referred to as a drain. Drains are privately owned and maintained as far as the boundary of the property. Beyond the boundary of the property a drain is referred to as a public lateral drain.
A pipe that serves more than one property is referred to as a sewer. Sewers that connect to the public sewer network are referred to as public sewers.
The sewer system, that is, the underground network of pipes that carries sewage (waste water and excrement), other waste water and surface water run-off, from properties to treatment facilities or other disposal points is referred to as sewerage.
Under the Public Health Act 1936 all sewers (as defined by the Public Health Act 1875) which were in existence on 1 October 1937 became public sewers. After 1937 new sewers were only public if they were laid or adopted by the sewerage undertaker.
However, on 1 October 2011 in England and Wales, private sewers and lateral drains that were connected to the public sewer before 1 July 2011 were transferred to the ownership of the regulated sewerage companies (generally water companies).
It is possible to apply for new or existing sewers or lateral drains to be adopted by a sewerage company. For more information see:
Public sewers usually run under roads or public open spaces, but they may also run through private property such as gardens. The sewerage company has a right of access to these public sewers in order to maintain them.
Permission is required from the sewerage company to build over a public sewer. Failure to obtain permission may result in the withholding of a building regulations completion certificate.
It is also possible to have public sewers diverted under Section 185 of the Water Industry Act.
The route of existing mapped public sewers can be determined by inspecting local authority records or by contacting the local sewerage company. There may also be details in property deeds. However, many public sewers are not mapped. In this case, it may be necessary to carry out inspections from manholes, to undertake an electronic sewer trace or to dig trial holes.
- A surface water drain or sewer is a pipe that carries only surface water, not foul water.
- A foul water drain or sewer is a pipe that carries waste water from a property such as from a toilet, bath, washing machine and so on. Surface water should not discharge into a foul water drain or sewer, as this can cause flooding of foul water.
- A rising main is a pressurised sewer that can be used to pump foul or surface water.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Cesspool.
- Clarified water.
- Difference between drains and sewers.
- Drainage.
- Drains.
- Grease management.
- Manhole.
- Private sewer.
- Public Health Act 1875.
- Safe working in drains and sewers.
- Sanitary pipework.
- Section 102 existing sewer adoption.
- Section 104 new sewer adoption.
- Septic tank.
- Sewer construction.
- Sewerage.
- Sewerage company.
- Sustainable urban drainage systems SUDS.
- Thames Tideway Tunnel.
- The redevelopment of Leicester's sewerage system by Joseph Gordon.
- Waste water.
Featured articles and news
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.






















