MASTRO Project - lifecycle costing and assessment in transport

|
| MASTRO - Intelligent Bulk Materials for Smart Transport Industries. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
BSRIA is taking part in the major European project supporting a shift towards smarter, safer and more sustainable transport.
[edit] MASTRO - Intelligent Bulk Materials for Smart Transport Industries.
Over the past 60 years, the EU transport industry has progressed substantially and continues to make a significant contribution to European prosperity, accounting for 4.5% of total employment in the EU and creating about the same percentage of gross domestic product. However, new developments in the relevant industries are needed to meet the EU goals by 2020 and 2050, as well as maintain and enhance the competitiveness of the European transport industry. The shift to smarter, safer and more sustainable transport through new developments in the automotive, aerospace and infrastructure industries is the main motivation of the MASTRO project. The project commenced in December 2017 and will be active for 3.5 years.
[edit] Project objectives and scope of research
The overall objective of the MASTRO project is to develop intelligent bulk materials for smart applications in the transport sector incorporating several self-responsiveness properties. The aim is to increase consumer safety, component life-span and performance, while reducing maintenance and manufacturing costs and through-life greenhouse gas emissions.
Self-responsiveness functionalities will be achieved by incorporating electrically conductive nanomaterials – such as multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphite-based nanomaterials – into smart lightweight polymer composites together with asphalt and concrete formulations. These self-responsive functionalities include the ability of the material to sense, heal, cure, protect, de-ice and heat.
MASTRO project objectives
The functionality of the intelligent bulk materials will be incorporated in various critical transport sector components, such as pavements, aircraft-wing leading edges and car bumpers. These components will be demonstrated under relevant conditions at prototype level for the aerospace, automotive and transport infrastructure sectors.
[edit] Project stakeholders
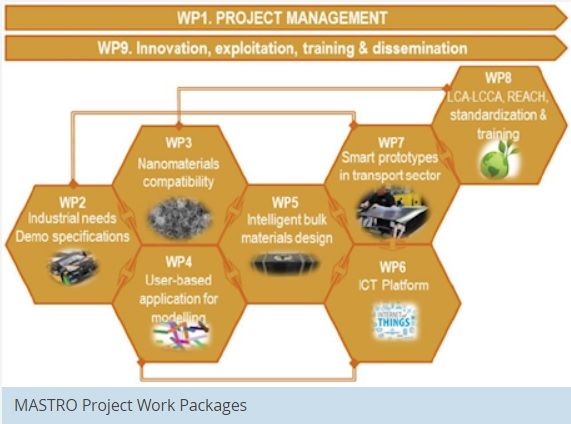
The MASTRO multidisciplinary consortium is made up of 17 partners from six EU countries, with a wide range of expertise: ACCIONA, ALKÈ, Applynano Solutions, ARKEMA France, AXIA Innovation, CETMA, CENTI, CITEVE, DIAD Group, Embraer Portugal, Le Centre Technique Industriel de la Plasturgie et des Composites, PINOUT Solutions, Superior Graphite Deutschland, Universitat d’ Alacant, Università degli Studi di Salerno and The University of Sheffield. It covers the whole value chain needed to achieve the main scientific and technological goals.
All the efforts devoted in the MASTRO project to fulfil its objectives can be grouped into the following tasks:
- BSRIA is leading a work package.
- Research activities developed at small- to medium-scale at laboratory environment.
- Up-scaling of the manufacturing processes, products and models, ending with prototype testing.
- Validation of the technologies developed according to the requirements and needs set by the end users.
- Activities focused on boosting the future market uptake.
|
[edit] BSRIA is leading a work package
BSRIA is involved in the project as leader of one of the nine work packages, responsible for the tasks which aim to demonstrate economic competitiveness and evaluate environmental impact of the new products in comparison with state-of-the-art practice.
In the first year of the project, BSRIA has successfully developed Life Cycle Costing and Life Cycle Assessment models of state-of-the-practice existing products, which will be used as a benchmark for comparison with the innovations of the MASTRO project. Additionally, within the same work package, other partners are working on activities related to the health and safety evaluation and regulatory compliance of MASTRO materials, as well as standardisation and training.
BSRIA has been recognised as one of the experts in the field of LCA and LCC modelling, having already successfully completed these activities on four EU-funded projects before. With the demonstrated knowledge and access to required tools, BSRIA is in a position to apply these processes to any product or system, be it nanomaterials, a commercial building or a HVAC system.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the grant agreement no 760940. The material presented and views expressed here are the responsibility of the author(s) only. The EC takes no responsibility for any use made of the information set out.
[edit] About this article
This article was written by BSRIA. It previously appeared on the BSRIA website in October 2019 and can be accessed HERE.
More articles by BSRIA on Designing Buildings Wiki can be accessed HERE.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Autonomous vehicles.
- Brexit - The case for infrastructure.
- Electric vehicles.
- Electro Conductive Concrete Ltd
- Government construction and infrastructure pipelines.
- Green infrastructure.
- Highway authority.
- Hyperloop
- Infrastructure.
- Integrated transport system.
- National Infrastructure Pipeline.
- Nationally Significant Infrastructure Projects.
- Railway engineering.
- Smart cities.
- Smart motorway.
- Sustainable transport.
- Traffic and transport.
- Transport design and health.
- Types of road and street.
--BSRIA
Featured articles and news
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.






















