How CAD to BIM Improve Collaboration and Efficiency in Construction Projects?
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The construction project process has changed since the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry adopted construction Building Information Modeling (BIM) in place of Computer-Aided Design (CAD). Using computer-generated drawings (CAD) instead of hand sketches increased both the process's speed and accuracy. Project data visualisation is entirely different now that BIM is in place, thanks to complex 3D models that more fully and precisely capture the project lifecycle.
The application of BIM has improved accuracy while simultaneously fostering more efficiency and collaboration. Planning, carrying out, and managing building projects have therefore significantly improved. To promote collaboration and boost efficiency in construction projects, this article will describe the CAD to BIM Conversion.
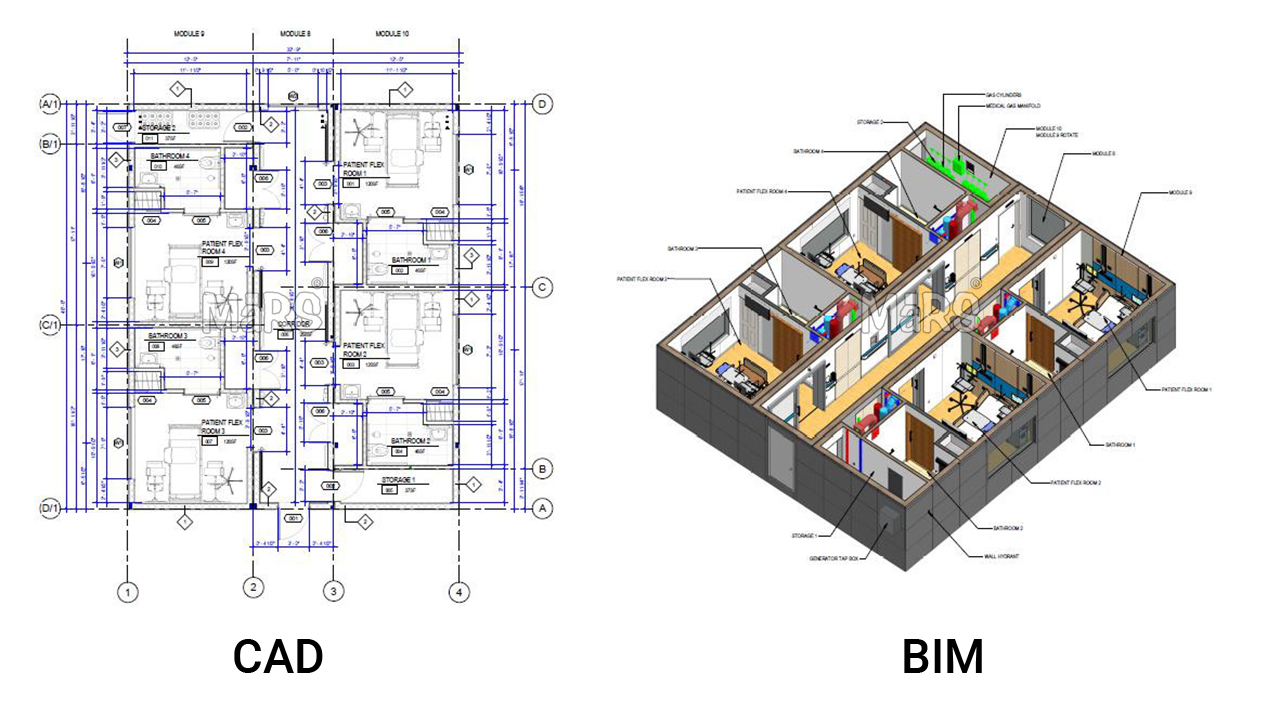
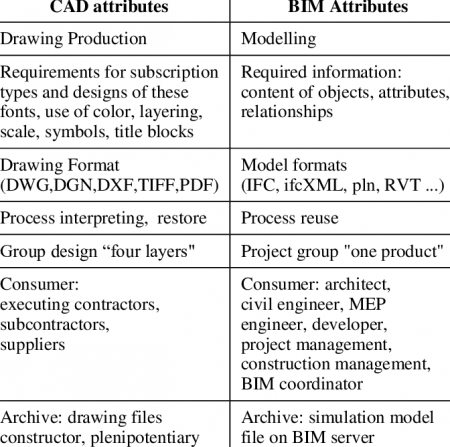
[edit] The Difference Between CAD and BIM
Computer-aided design, or CAD, enables the development and documentation of complex structures. Over the last 30 years, it has altered the building industry by transitioning from manual drawings to computer-generated design documentation, facilitating complex elements to be built with greater efficiency. AEC, aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and plant design experts, among others, have heavily embraced CAD software to meet construction standards and decrease product launch times.
When it comes to BIM, it is a process in which architects, contractors, and engineers work on a common database and computer model. The facility, complete with functional systems and aesthetics, is represented digitally. Project development can be carried out effectively and cooperatively thanks to the joint use of BIM by many professions. Design-to-construction workflow re-engineering and a greater emphasis on BIM software tools are being seen by contractors and architectural and engineering design firms these days.
The adoption of new software tools and methods allows designers to uncover design flaws before construction begins, avoiding costly modification orders. Thus, BIM is predicted to take over, replacing 2D CAD for real-time model analysis and 3D visualisation.
[edit] An Evolution from CAD to BIM
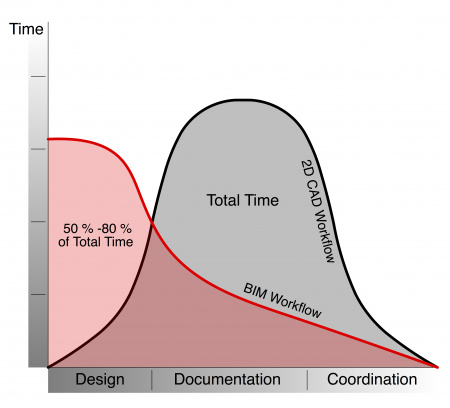
Traditional CAD solutions failed to satisfy major construction projects' demands due to limitations in collaboration and information management. These problems arise generally in complex projects, resulting in reduced efficiency and mistakes, expanding project expenses, and limited stakeholder coordination.
BIM provided the solution to these problems, enabling 3D parametric modelling and comprehensive data. BIM may entail numerous aspects like 4D time and 5D cost to give a complete solution for the whole building life cycle. The shift from CAD to BIM denotes an evolution heading for a more integrated, effective, and collaborative outlook in the design, engineering, and construction sectors.
[edit] Advantages of BIM versus CAD in the Construction Industry
BIM offers substantial benefits compared to two-dimensional CAD in the construction industry because it is a digital representation that can be utilised at any point; however, CAD drawings are fixed and only convey limited data. The key advantages of BIM over CAD are:
[edit] Real-time 3D Visualisation
Building information modelling allows for simulations of how space will be used and visual representations before construction begins. This strategy encourages well-informed determinations while preventing delays and unneeded alterations by enabling all involved parties to cooperate in real time. Observing development as the project advances generates records and aids in visualising how far along the project has come.
[edit] Accurate cost estimates
Designers find it easier to access data in a model, which is often in the form of reports giving material quantities and cost estimates. Construction plans based on BIM-generated models allow for quick and accurate assessment of raw materials and resources while also providing practical insights into project implementation.
Stakeholder Collaboration
BIM is a cloud-based platform facilitating collaboration and teamwork between teams across locations. BIM's capacity for data integration brings together data from numerous sources, advancing choice-making, coordination, and project proficiency enabling stakeholder communication.
[edit] Facility Management and Operations
While CAD drawings may not offer information, for facility management BIM-based building models empower facility managers post-construction. Accurate cost estimation and digital documentation are crucial, for handover and effective upkeep. BIM-based building models offer estimates and digital documentation enhancing the efficiency of facility management.
[edit] Early Risk Identification and Safety Concerns
Before construction starts, BIM offers a thorough project overview that promotes stakeholder engagement. It aids in risk identification and loss prevention from labour shortages, material waste, and legal troubles. Moreover, BIM aids engineers and architects in locating risk areas and putting safety precautions in place to reduce threats to health and safety.
[edit] Considerations while Transitioning from CAD to BIM
Making the transition from CAD to 3D BIM may seem daunting due to the abundance of options. The following factors should be taken into account when choosing the ideal program:
- Accuracy of 2D and 3D drawings
- Capability to define properties
- Capability to make reports
- Visualisation skills
[edit] Wrapping Up
To ensure productivity, the shift from CAD to BIM is a significant one that must be made carefully. With the use of BIM, organisations in the AEC sector may accurately, efficiently, and collaboratively manage the whole lifespan of a construction project. Thus, it can be concluded that BIM is a crucial industry component since it facilitates collaboration and efficiency procedures from design to maintenance.
BIM Directory
[edit] Building Information Modelling (BIM)
[edit] Information Requirements
Employer's Information Requirements (EIR)
Organisational Information Requirements (OIR)
Asset Information Requirements (AIR)
[edit] Information Models
Project Information Model (PIM)
[edit] Collaborative Practices
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC)