Health and Safety Regulations Construction Managers Must Follow
Safety is as crucial as the foundation of a high-rise building. Imagine, if you will, the dynamic and often chaotic construction site where every day brings a new challenge. It's here that construction managers become the unsung heroes, juggling not just blueprints and deadlines but also a hefty portfolio of health and safety regulations.
Let’s unravel these rules one by one to understand how they help keep the hard hats on and the injuries out.
[edit] The Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992
Under the Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992, it's not just about distributing the right gear; it's ensuring that each item fits well, is properly maintained and is suitable for the specific tasks at hand.
This straightforward rule—equip and train your team correctly—helps keep your project moving smoothly and safely. PPE safety training is essential, much like suiting up in superhero gear every day. This mandatory training includes equipping construction workers with hard hats, safety goggles and high-visibility vests.
[edit] Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
Planning is everything, isn't it? The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 think so, too. These regulations require managers to get up to date with risk assessments and lay out clear plans to mitigate risks. It's about knowing what could go wrong and having a solid game plan to prevent it. Regular training sessions? Check. Emergency procedures? Check. This regulation ensures that preparedness is a priority.
[edit] Construction Design and Management Regulations 2015
Talk about getting everyone on the same page! CDM 2015 is all about integrating health and safety into the building design from the get-go. It ropes in everyone from architects to engineers, ensuring that safety is not an afterthought. This proactive approach helps identify risks early and design them before they become real problems on-site. It’s a brilliant strategy to keep safety as a cornerstone of construction projects, big or small.
[edit] Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations 1998 (LOLER 1998)
LOLER regulations are vital for managing lifting operations, which can be complex and risky. The Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) 1998 mandate that all lifting equipment, whether it's a crane's lifting beam or a forklift moving materials, must be safe, sturdy and suitable for use.
Proper LOLER training is critical to preventing those heart-stopping moments on the job. This training ensures that everything is certified and fit for purpose, with regular checks and balances to minimise the risk of accidents, such as unexpected falls of lifted loads.
[edit] Work at Height Regulations 2005
Heights can be daunting and falling from them doesn’t bear thinking about. The Work at Height Regulations 2005 make sure that any work above ground is planned, supervised and, most importantly, safe. It’s about choosing the right equipment and using it right. From scaffolding to ladders, each choice must be justified with safety in mind, ensuring that gravity remains a friend, not a foe.
[edit] Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) Regulations 2002
Chemicals on site? Handle with care! COSHH 2002 ensures that all hazardous substances are identified and managed with utmost care. This includes everything from the paint to the cleaning agents used on-site. Proper storage, correct handling procedures, and emergency measures are all part of this package, and it aims to prevent any chemical mishaps that could put workers at risk.
[edit] Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
They say it’s all in the lift. And with the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992, it’s about lifting correctly to avoid injuries. Training workers on how to handle loads properly helps reduce the risk of back injuries, one of the most common ailments on construction sites. It’s about innovative work, not hard work.
[edit] Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 2013 (RIDDOR 2013)
When things go south, RIDDOR 2013 ensures that they’re not swept under the rug. This regulation requires that all injuries, diseases and dangerous occurrences are reported. It’s an essential part of understanding what’s going wrong and preventing it in the future. Think of it as the construction world’s feedback system, pivotal for continuous improvement.
[edit] Concluding Remarks
Ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations is a critical responsibility for construction managers. This article is intended for educational purposes only and does not provide an exhaustive list of regulations Construction Managers must follow. Construction managers must always stay informed and adhere to all applicable laws and regulations specific to their projects and locations to maintain a safe working environment.
Featured articles and news
Key points for construction at a glance with industry reactions.
Functionality, visibility and sustainability
The simpler approach to specification.
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
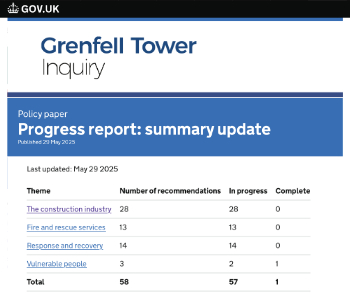
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.