Earth to air heat exchangers
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
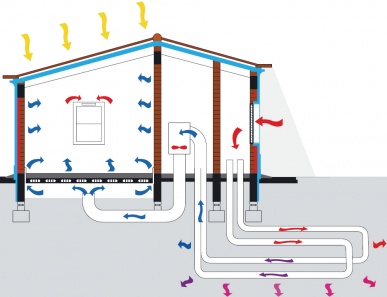
An earth-to-air heat exchanger draws ventilation supply air through buried ducts or tubes. As the temperature of the ground below 3m is practically constant, it substantially reduces ambient air temperature fluctuations. It therefore provides space conditioning throughout the year, with the incoming air being heated in the winter and cooled in the summer by means of earth coupling.
[edit] System options
Systems can be driven by natural stack ventilation, but usually require mechanical ventilation. In some cases air is circulated via air handling units, allowing filtering and supplementary heating/cooling. A simple controller can be used to monitor inlet and outlet temperatures, as well as indoor air temperatures. Ground coupling ducts or tubes can be of plastic, concrete or clay – the material choice is of little consequence thermally due to the high thermal resistance of the ground.
Earth-to-air heat exchangers are suited to mechanically ventilated buildings with a moderate cooling demand, located in climates with a large temperature differential between summer and winter, and between day and night. Location of the ducts in sand or gravel below the water level, where there is moving ground water, gives the best performance, however, the presence of ground water involves extensive sealing precautions.
[edit] Size and output
The optimum pipe length is a function of pipe diameter and air velocity. Small pipe diameters of between 200 and 300mm are thermally more efficient. Pipes should be buried at a minimum
depth of 2m and separated by 1-2m to allow heat dissipation. The optimum air velocity is typically 2m/s.
Under constant load, the cooling capacity of the ground may become exhausted and, therefore, generally it is not possible to meet high loads. With high loads, two separate duct systems could be considered – one for use in the morning and one for use in the afternoon.
A bypass can be used to improve the performance of the system during periods when the ambient air temperature can meet the cooling requirements. In unoccupied periods when the ambient air temperature falls below the surface temperature in the ducts, night cooling can be used to pre-cool the system.
The ground temperature is based on ‘undisturbed’ conditions. When the ducts are installed beneath the building, or even within a built up area, this will be affected substantially. The effect that the duct has on the ground temperature also needs to be considered. Optimisation of the design requires a complete thermal simulation of the system.
In principle, these are low-cost systems – the excavation is the major part of the installation cost. Maintenance is minimal, but regular inspection and cleaning of the ducts is recommended.
[edit] Summary
Earth-to-air heat exchangers can be used on new buildings or refurbishments to provide free cooling in the summer and pre-heating of air in the winter. They have high capital costs, but over the life of the system can yield substantial savings.
This article was created by --Buro Happold 17 March 2013, based on a 2008 article in 'Patterns'.
[edit] Related articles
- Coefficient of Performance CoP.
- Dynamic thermal modelling of closed loop geothermal heat pump systems.
- Geothermal energy.
- Geothermal pile foundations.
- Ground energy options
- Ground preconditioning of supply air.
- Ground source heat pumps.
- Renewable energy sources: how they work and what they deliver: Part 3: Electrically driven heat pumps DG 532 3.
- Thermal labyrinths.
Featured articles and news
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this.