Causes of sinkholes

|
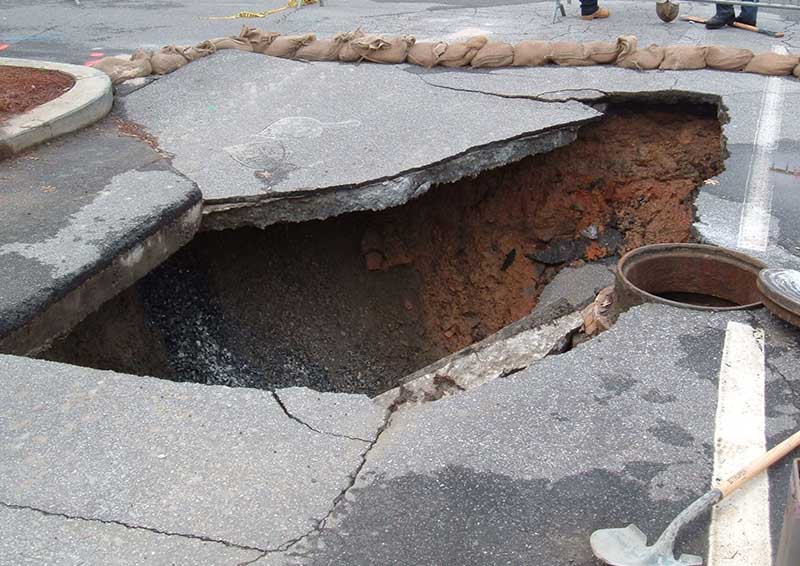
| Sinkholes opening up in the middle of cities. |
A huge sinkhole swallowed a bus, killing six people in Northwest China in January 2020, sparking an electrical explosion and leaving several missing. Several people disappeared as the sinkhole spread and 16 people were taken to hospital.
Sinkholes are not uncommon in China and experts cite the country's rapid pace of huge construction work as one of the triggers.
Watch the BBC footage of the latest incident.
Dr. Clive Edmonds is a geotechnical specialist and has studied sinkholes for the past 30 years.
"The main trigger for sinkholes is water," says Dr. Edmonds. "In 90% of sinkhole cases, water saturating the mineral deposits is the main trigger, known as Karst processes.
"Sinkholes happen when a layer of rock underneath the ground is dissolved by water. In regards to China and their sites, I know there there are some Karst problems with limestone deposits.
"Sinkholes depend on geometry, some rocks are more soluble than others - salt deposits for instance dissolve more quickly. Gypsum for instance is a very soluble rock. Chalk and limestone deposits may take thousands of years to dissolve but when new cavities occur they can cause spectacular sinkholes."
"Human development can contribute greatly, especially construction work in urban areas where you may have dense development with roadworks, etc, as in the case of China. The surface becomes impermeable with water collecting over time in drains and sewers - water starts leaking into the ground."
"There are warning signs you can spot. First indicators are dips and depression in the ground surfaces, deepening with tiny cracks in pavements or buildings for instance, leading to buildings showing slight movement. "
Tunnelling into water filled cavities or where water bodies can flow catastrophically into an excavation are particularly hazardous.
"In the UK any such instances have been caused by small cracks in the ground leading to the onset of building movement and then a breakdown in the water utilities or leak of a mains water pipe or a sewer eventually draining water into the ground.
In the UK there has been a long history of mining and water abstraction, which in some areas has left a legacy of man-made cavities. The term sinkhole is, in the UK, often extended to cover the collapse of ground into such man-made features.
But predicting a sinkhole collapse is not easy as there can be very little surface evidence of the features.
Tony Bracegirdle is a senior partner of the Geotechnical Consulting Group.
"There are seldom warnings in urban areas," says Tony, "although sometimes sinkholes develop slowly to the extent that there is sufficient time to restrict access. Sinkholes tend to focus in specific geological and topographic conditions and so the hazard can be reasonably quantified in areas where there is a history of recurring sinkhole activity"
"The most common response in high-risk locations is to design works that are insensitive to potential sinkholes," says Tony, "to control surface water and to take additional precautions to limit water loss from drains and services."
What can civil engineers do to prevent sinkholes?
[edit] About this article
This article - written by ice.org.uk Andrew Panos of the Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) - previously appeared on the ICE website in January 2020 under the title 'What are the causes of sinkholes'. It can be accessed HERE.
Other articles by the ICE on Designing Buildings Wiki can be accessed HERE.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Contingency plan.
- Design risk management.
- Health and safety.
- Interface risk in construction.
- Method statement.
- Near miss.
- Principles of prevention.
- Project risk.
- Retained risk.
- Risk assessments and method statements.
- Risk assessment.
- Risk feedback.
- Risk management.
- Risk register.
- Safety management.
- Surfside condo collapse: climate change demands adaptation in design and approach.
- Value management.
- What is a hazard?
Featured articles and news
Retired firefighter cycles world to raise Grenfell funds
Leaving on 14 June 2025 Stephen will raise money for youth and schools through the Grenfell Foundation.
Key points for construction at a glance with industry reactions.
Functionality, visibility and sustainability
The simpler approach to specification.
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
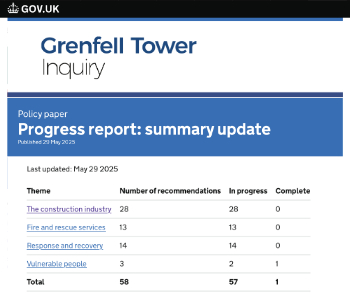
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.