Hyperbolic paraboloid in construction
|
|
|
|
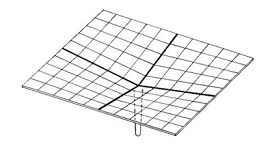
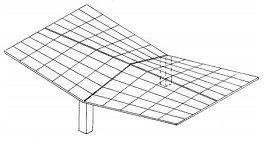
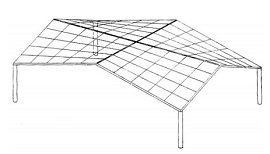
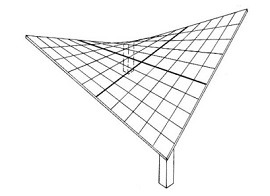
A hyperbolic paraboloid (sometimes referred to as ‘h/p’) is a doubly-curved surface that resembles the shape of a saddle, that is, it has a convex form along one axis, and a concave form on along the other. It is also a doubly-ruled surface, that is, every point on its surface lies on two straight lines across the surface. Horizontal sections taken through the surface are hyperbolic in format and vertical sections are parabolic.
The fact that hyperbolic paraboloids are doubly-ruled means that they are easy to construct using a series of straight structural members. As a consequence they are commonly used to construct thin ‘shell’ roofs. These can either be formed using timber or steel sections, that are then clad, or they can be constructed using concrete.
The use of hyperbolic paraboloids as a form of thin shell construction was pioneered in the post-war era, as a hybrid of modern architecture and structural engineering. Being both lightweight and efficient, the form was used as a means of minimising materials and increasing structural performance while also creating impressive and seemingly complex designs.
Rather than deriving their strength from mass, like many conventional roofs, thin shell roofs gain strength through their shape. The curvature of the shape reduces its tendency to buckle in compression (as a flat plane would) and means that they can achieve exceptional stiffness. Being braced in two directions they experience no bending and are able to withstand unequal loading, whether from dead loads (such as equipment hung from the ceiling), or live loads (such as wind).
Hyperbolic paraboloid shell roofs can be constructed using reinforced concrete with a shell thickness of just 50 mm for diagonal spans up to 35 m.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Anticlastic.
- Arches.
- Barrel vault.
- Cantilever.
- Catenary.
- Concept structural design of buildings.
- Conoid shell.
- Folded plate construction.
- Long span roof.
- Megastructure.
- Pendentive dome.
- Portal frame.
- Shell roof.
- Structural engineer.
- Synclastic.
- Tensegrity.
- Tensegrity bamboo pavilion
- Tensile structures.
- The development of structural membranes.
- Types of dome.
[edit] External resources
- ‘Building Construction Handbook’ (6th ed.), CHUDLEY, R., GREENO, R., Butterworth-Heinemann (2007)
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.



















