Town and Country Planning (General Permitted Development) (Amendment) (England) Order
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Generally it is up to a local planning authority to decide whether to allow a particular development or not. However, in England and Wales, the Town and Country Planning (General Permitted Development) Order 1995 enables central government to permit certain types of developments known as permitted developments. These are generally minor changes to existing properties.
Permitted developments do not require approval from the local planning authority as permission is granted by the Order. Examples of permitted developments include: certain enlargements or alterations to houses; certain pet enclosures, sheds and fuel storage containers; certain porches, doors and windows, and so on (see permitted developments for more information).
In May 2013, the Town and Country Planning (General Permitted Development) (Amendment) (England) Order 2013 came into force, making changes to permitted development rights.
[edit] Use class change
The Order allows change of use class from Offices B1(a), to Residential C3. However, it is still necessary to apply to the local planning authority to determine whether prior approval is required for other matters is still (for example, contamination, flood risk, transport and highways).
In addition, if the change of use requires any alterations to the building that are not permitted developments then these alterations will still require planning permission. Some areas, such as conservation areas, the Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, London Central Activities Zone and Tech City, and Manchester City Centre Core are excluded from the amendment (see Government maps of exempt areas). The change of use must take place before 30 May 2016.
The thresholds for change of use between B1, B2, and B8 have been increased from 235 - 500 sq. m.
A two year, temporary change of use is allowed for buildings of 150 sq. m or less from A1, B1, D1 and D2 to A1, A2, A3 and B1.
Subject to prior approval, business premises, assembly and leisure centres, residential institutions and hotels are permitted to change use to state funded schools and vice versa.
See Use Class for definitions of use classes.
[edit] Extensions
The order increases permitted development rights for single-storey (less than 4m in height) rear extensions from 4m to 8m for detached dwellings, and from 3m to 6m for other dwellings, if the dwelling is not in an exempt area and the extension does not cover more than 50% of the curtilage of the dwelling. The local planning authority will use ‘a light-touch neighbours’ consultation scheme’ and will assess whether prior approval is required. The works must be completed by 30 May 2016.
In addition, extensions of 100 sq. m or 50% (whichever is lower) are permitted for offices, shops and professional and financial services. Extensions of 200 sq. m or 50% are permitted for industrial premises. The works must be completed by 30 May 2016.
[edit] Prior approval
Some of these amendments permit development only with prior approval of certain aspects or beyond certain sizes. See prior approval for more information.
[edit] Ongoing changes
Further changes to the rules for permitted development are ongoing with continual policy changes. See Permitted development for more information.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Article 4 direction.
- Growth and Infrastructure Act.
- National planning policy framework.
- Permitted development.
- Planning permission.
- Prior approval.
- Town and Country Planning Act.
- Use class.
[edit] External references
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
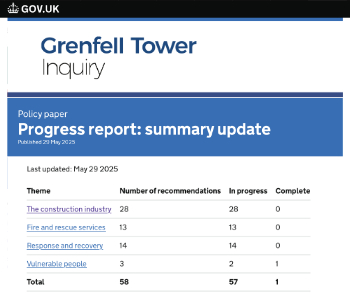
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.