The structural behaviour of architectural fabric structures
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
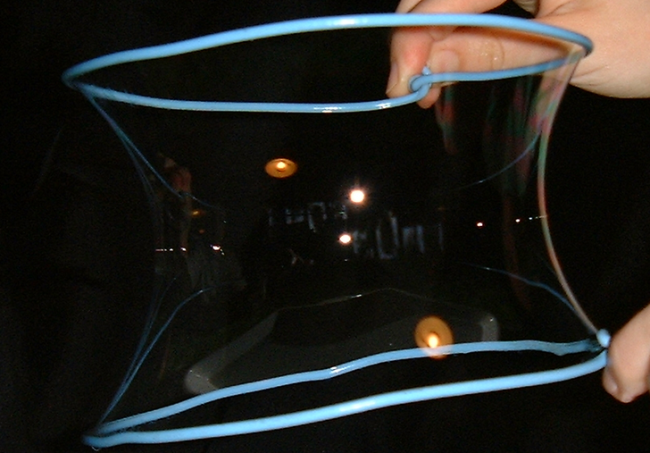
Fabric structures are a form of tensile structure in which a membrane is 'stretched' to form a structurally stable surface. Typically, the membrane is formed by a fabric, consisting of a woven base cloth, coated on both sides with an impermeable polymer, and sometimes a durable topcoat, held in position by tension forces imposed by a structural framework, a cabling system, internal air pressure or a combination.
[edit] Architectural fabrics.
Typically, fabric structures are formed using PTFE coated glass, or PVC coated polyester, although there is an increasingly wide range of other materials available. For more information see: The development of structural membranes.
The fabric itself it generally very thin, approximately 1mm thick. It has very little compressive strength, but very high tensile strength. Woven glass fabrics are stronger in tension than steel. Different types of membrane are available depending on the use, longevity and tensile strength required.
Typical tensile strengths are set out below:
- Type 1: 3,000 N/5cm
- Type 2: 4,000 N/5cm
- Type 3: 5,550 N/5cm
- Type 4: 7,000 N/5cm
- Type 5: 9,000 N/5cm
Individual pieces of fabric may be welded, heat sealed, glued or sewn together to form larger panels. Steel cables may be attached to the perimeter of the panels, to pull them into their desired positions.
[edit] Structural form
Fabric structures are generally tensioned and given their structural stability by their doubly-curved shape, which may be anticlastic or synclastic.
|
|
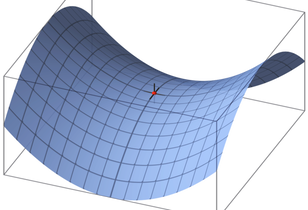
[edit] Anticlastic
An anticlastic surface (or a saddle shape), is a surface in which the two axes of the surface curve in opposite directions, that is, the centres of curvature are located on opposite sides of the surface. A hyperbolic paraboloid is an example of an anticlastic surface.
Anticlastic shapes tend to be formed by steel cables and masts or arches pulling them into tension. Whilst the fabric itself may be very thin, the tensile force imposed on it to ensure it remains stable under load can be high, and so the supporting structure required to transfer loads to the foundations can be significant.
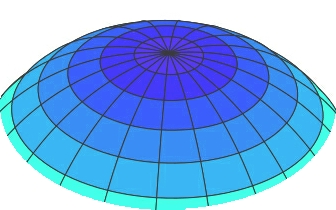
[edit] Synclastic
A synclastic surface (or a dome shape), is a surface in which the two axes of the surface curve in the same direction, that is the centres or curvature are on the same side of the surface.
Synclastic surfaces are typically created by inflation (sometimes referred to as air-supported structures). Air pressure within the enclosure maintains the form of the surface when it is tensioned. The is similar to blowing up a balloon, but the pressure is very low so that it is generally not noticeable to occupants.
[edit] The effect of curvature
Doubly-curved surfaces can be tensioned without distorting their form, as the opposing curvatures balance each other at every point on the surface. Tensioning the fabric reduces its elasticity so that it will distort less when subsequently loaded, such as under wind load or snow load.
In addition, the geometry of the curvature itself means that any extension of the fabric under load results in a relatively smaller deflection than would be apparent in a flatter, or less curved fabric.
So the greater the curvature and the greater the pre-tensioning of the fabric, the less it will distort under load.
[edit] Structural design
A range of techniques can be used to design and analyse the stressed skin of fabric structures and to determine the optimum structural shape.
This process was initially carried out using relatively simple mathematical techniques and model making using wire frames and soap films to determine optimum forms, sometimes described as ‘minimal surfaces’.
It is only relatively recently that it has been possible to model the non-linear, dynamic behaviour of architectural fabrics (in which a change in one part affects all other parts and vice versa) using specialist form-finding software. This allows designers to vary the elements, boundary conditions and geometry of the design and rapidly determine the most efficient structural solution.
This software can also be used to generate patterns for automatically cutting the fabric panels to create the form required.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Anticlastic.
- Architectural fabrics.
- Carbon fibre.
- ETFE.
- Fabric structures.
- Polyvinyl chloride PVC.
- Principles of enclosure.
- PTFE.
- Structural principles.
- Tensile structures.
- Thermal behaviour of architectural fabric structures.
- The history of fabric structures.
- The development of structural membranes.
- The thermal behaviour of spaces enclosed by fabric membranes.
Featured articles and news
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.