Reverberation in buildings
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Sound is caused by vibrations which transmit through a medium such as air and reach the ear or some other form of detecting device. Sound intensity is measured in Decibels (dB). This is a logarithmic scale in which an increase of 10 dB gives an apparent doubling of loudness.
Approved document E, Resistance to the passage of sound defines 'Reverberation' as the persistence of sound in a space after a sound source has been stopped. Reverberation time is the time, in seconds, taken for the sound to decay by 60dB after a sound source has been stopped.
The reverberation time of a room is linked to the the surfaces that enclose it and the volume of the room by the Sabine equation:
RT = Volume x 0.161 / Total Acoustic Absorption
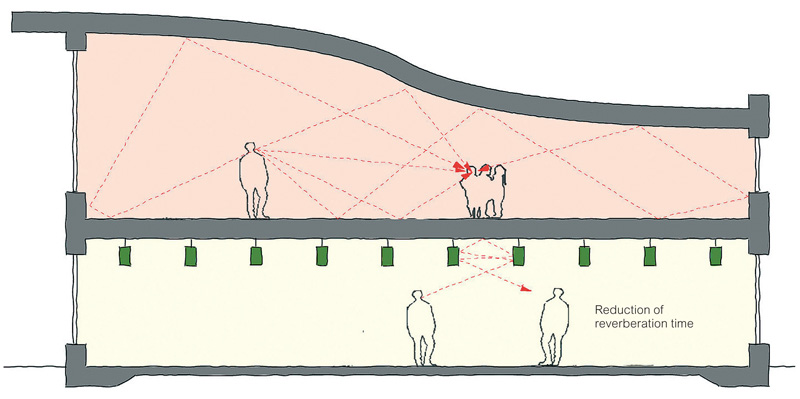
Image: To control reverberation time, acoustic absorption is used.
Room acoustics / reverberation affects the way a space sounds. A high reverberation time can make a room sound loud and noisy. Speech intelligibility is also a function of reverberation, a high reverberation time causes speech to sound muffled and muddy. Rooms designed for speech therefore typically have a low reverberation time: ≤1 second. A high reverberation time can enhance a music hall by adding richness, depth and warmth to music. A higher level of reverberation within a concert hall is therefore critical.
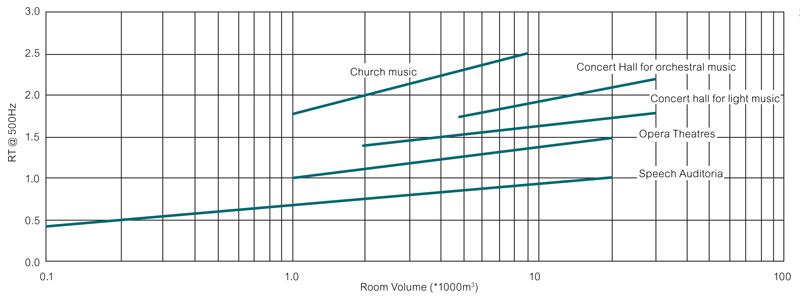
The illustration below provides indicative reverberation times for a range of building types and room volumes.
[edit] Acoustic properties of materials
To control reverberation time, acoustic absorption is used. Absorbent materials conventionally take two forms; fibrous materials or open-celled foam. Fibrous materials absorb sound as sound waves force the fibres to bend and this bending of the fibres generates heat. The conversion of acoustic energy into heat energy results in the sound effectively being absorbed. In the case of open-celled foam, the air movement resulting from sound waves pushes air particles through the narrow passages which in turn generate a viscous loss along with heat.
Architecturally, fibrous materials and open celled foams are not always considered attractive or robust. It is common therefore to cover these materials with an acoustically transparent finish such as a tissue, cloth or slatted wood, or with perforated materials such as wood, metal, plasterboard and so on.
The thickness of a given material along with properties such as its fibrousity governs its acoustic performance. Finishes within a space are defined in terms of their absorption coefficient. This is a number between 0.0 (100% reflective) for example stone, tiles or concrete and 1.0 (100% absorbent), for example high performance acoustic ceiling tiles, slabs of mineral wool, etc. Products such as carpets typically have an absorption coefficient between 0.1 and 0.3 depending on their thickness. Perforated plasterboard generally provides around 0.6 to 0.7.
It is also common to classify absorbent materials in categories, A to E, where A is highly absorbent and E is almost fully reflective.
This article was created by --MACH Acoustics 11:04, 28 November 2013 (UTC)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Airborne sound.
- Approved Document E.
- Building acoustics.
- Building Bulletin 93: acoustic design of schools.
- Decibel.
- Flanking sound.
- Impact sound.
- Noise nuisance.
- Robust details certification scheme.
- Room acoustics.
- Sound insulation.
- Sound absorption.
- Sound frequency.
- Sound insulation testing.
- Sound power.
- Sound v noise.
- Noise nuisance.
[edit] External references
- MACH Acoustics: Room acoustics and reverberation.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.