How technology can support social distancing
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the world as we know it is changing. The bottom line is that buildings are not going to be able to reopen and operate safely without robust, post-pandemic planning for pedestrian movement.
Real people get confused and break rules. It is one thing to hang signs and tape lines and crosses to the floor, but will people stay in their boxes and comply with the rules? Will they have real fear of proximity?
Knowing how to manage your space as guidelines ease, or if the Government asks you to double down again overnight in the face of new waves of infection, is vital.
[edit] Designing with social distancing in mind
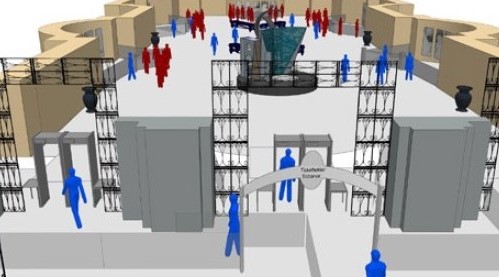
It will come as a relief to learn that raw materials for greater certainty, and the flexibility to keep up with a dynamic situation over the months, and possibly years, are all readily available. The likes of 2D and 3D CAD drawings for your building can be used to render a 3D model of the building which can be populated with realistic, intelligent agents whose behaviour is modelled by pedestrian movement software.
One example of technology that can be used to help map social distancing in a building is MassMotion. It is rather timely that the software world’s ubiquitous move towards subscription rather than outright licensing has come just as professionals across the built environment are grappling with the need to understand pedestrian behaviour in greater detail than ever before.
Its proximity modelling tests and visualises scenarios within computer models. Its native 3D design means that crucial potential pinch points (like stairs and elevators) are also modelled accurately and can be observed in animated visualisations.
Its sheer power means that new parameters can be entered into the model and a new simulation will run to test new ideas within minutes. Proximity modelling tools are used to show how close people are likely to get - and for how long - and highlight risk areas.
Oasys added proximity modelling to its pedestrian simulation software and explained, “What the team has done is to produce a new set of analytics that can be drawn from the software. We have also accelerated some experimental research to give customers the ability to test personal space preferences.”
[edit] Technology for existing buildings
Technology such as MassMotion will be crucial in designing and building future structures to ensure social distancing is far more achievable for the building’s occupants. How can other technological solutions help support social distancing measures in pre-existing buildings? After all, spatial awareness cannot be accurately relied upon.
Personnel distancing systems (known as PDS) are being trialled around the country. These proximity warning gadgets can be fastened to a person’s arm or belt, or in the case of construction sites, onto a hard hat. The technology can also be added to lanyards or wrist bands. Once the exclusion zone has been programmed, these tags will sound an alarm and vibrate if the wearer gets too close to another wearer.
This technology will be particularly useful in warehouses and shops, allowing staff in a highly mobile environment to focus on their jobs around the building and let the PDS alert them if social distancing measures are being breached.
[edit] The future of building management
Understanding and optimising how people use space is increasingly recognised by designers, but can it also inform smart environmental and energy management? As well as wearable smart sensors for people, there have been innovative smart sensors for buildings that detect the number of occupants in a space. This would suggest that there is a growing overlap here.
Pedestrian movement analysis could be a long-term addition to our toolbox, not just an interim response to the pandemic.
This article originally appeared in the Architectural Technology Journal (at) issue 135 published by CIAT in fall 2020. It was written by mediaworks on behalf of Oasys.
--CIAT
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.