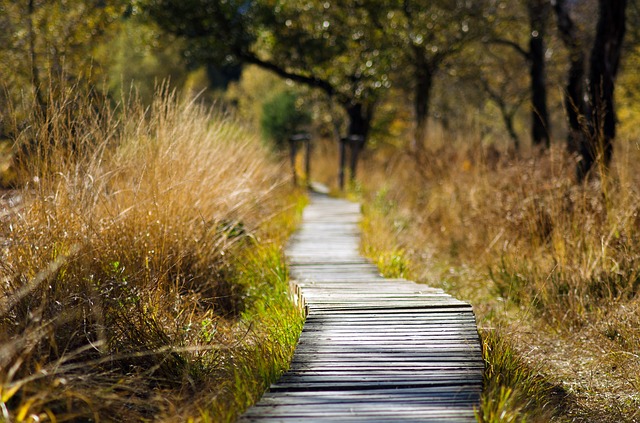
Helping to make Europe a wilder place
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Rewilding advocates have invited civil engineers to help upgrade Europe’s significantly damaged ecosystems. Paul Jepson of UK environmental consultancy Ecosulis says the profession is vital to successful rewilding.
[edit] Conservation in the spotlight
European rewilding practitioners called on civil engineers and other progressive professions to join a collaborative effort to recover nature and create a wilder Europe. The online appeal in November 2019 was a response to the realisation that natural values are close to ground zero in western Europe.
The reality is entering the public consciousness through media reporting of the huge declines of insects, revealed by the windscreen ‘splatometer’ test, and the plummeting numbers of once-common species reported in recent State of Nature Reports. The situation is contributing to a sense of alarm and despondency in society and anger that public institutions appear unable to turn things around.
However, the call also signified a move from the defensive nature-protection logic of the twentieth century to a more confident, hopeful and innovative approach to conservation. Rewilding views nature as a force with the capacity recover if the conditions are engineered for it to do so.
[edit] Upgrading ecological infrastructure
Rewilders need help with designing and steering new ecological infrastructure and nature-based solutions to challenges and opportunities associated with accelerating social, technological and economic change. While they have exciting and ambitious nature recovery visions, they know change requires collaboration and co-design with professionals across multiple sectors – particularly civil engineers.
The global rewilding movement takes its inspiration from multiple past baselines to upgrade ecosystems within the constraints of what is possible. It is guided by the functional ecology and insight that biodiversity, bio-abundance and ecological resilience are emergent outcomes of interactions between three components of nature: trophic complexity (the ‘web-of-life), natural disturbance and natural dispersal.
[edit] Ecological connectivity
The interface between the civil and ecological engineering professions has already made valuable contributions to enhancing ecological connectivity. Examples include integrating eco-bridges into linear infrastructure design, and restoring natural river dynamics to reduce flood risk and create new natural assets with recreational, identity, tourism and ecological value.
There is great potential to build on this progressive practice. For example, infrastructure projects invariably involve physical disturbance of land, yet current practice is to put this right by following highly specified and site-specific ecological restoration designs. Given new understandings of the value of ‘messy chaos’ to the ecological function of landscapes, future civil engineering projects might generate a succession’ of ‘pop-up’ habitat transitions from bare-ground through scrub to woodland.
More ambitiously, civil engineering could contribute to landscapes that enable the reassembly of an array of large herbivores − wild cattle, horses, deer and pigs − that are now known to be central to the web-of-life and foremost agents of ecological recovery. This would require a mix of foresight and planning that identifies connections and synergies between different projects.
[edit] Decade of restoration
The United Nations has declared 2021−2030s the decade of ecosystem restoration, and the EU is expected to respond with ambition new restoration targets in its new biodiversity strategy 2030.
In the UK, new environment and agricultural bills are guided by political commitments to create the first generation of people who leave the environment in a better place than they found it. Rewilders are calling on all sectors to join in creative and ambitious thinking on how to do this.
This article is based on the authors’ briefing article in the 173 CE2 of the ICE Civil Engineering journal. It was published on 1 May 2020 on the ICE Civil Engingeer Blog and was written by Paul Jepson of Ecosoulis.
--Institution of Civil Engineers
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.