Scarp
|
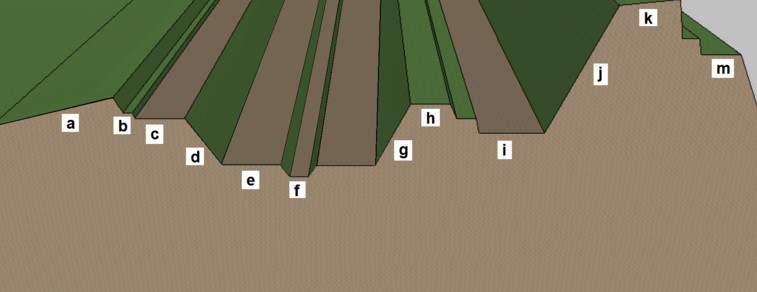
A section through the ditch and rampart of a typical early modern artillery fortification (16th to 19th centuries). The elements are: a) glacis, b) banquette, c) covered way or covertway d) counterscarp, e) ditch, f) cunette, g) scarp, h) faussebraye, i) chemin de ronde, j) rampart (exterior slope), k) parapet, m) terreplein. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
As a form of medieval military fortification, a scarp (also referred to as escarp or escarpment) was a term used to describe the inner slope of a defensive ditch. The outer portion of the slope or ditch was referred to as the counterscarp. Scarp and counterscarp defensive fortifications were built below grade - but visible to attackers - and adjacent to a moat or ditch.
NB With respect to modern topographic wind effects, the term escarpment, is defined by the ICC’s 2018 International Residential Code, as ‘a cliff or steep slope generally separating two levels or gently sloping areas.’
[edit] History
Scarp and counterscarp structures were introduced as a form of military defence in the 1500s. The technique was developed by Italians as a form of protection against enemies using cannons in their attacks.
As existing defensive walls were compromised, a technique using sloping ramparts was first used in Pisa in 1500. This method was tested to protect vulnerable areas from French attacks.
[edit] Improvements by Fra Giovanni Giocondo
The angled rampart proved more effective against cannon fire, and a few years later, the method was further advanced by Fra Giovanni Giocondo, a monk who had trained as an architect, draughtsman and engineer. Fra Giocondo was also involved in municipal engineering projects - such as road construction and bridge foundations (including the Pont Notre-Dame in Paris) - and was part of the team involved with the construction of the foundation piers of St. Peter's Basilica.
With extensive knowledge developed through his archaeological studies, Fra Giocondo was called upon by officials in several cities around Europe. During this period, he was asked to provide advice on military fortifications, which is when he proposed the idea of scarp and counterscarp fortifications. Fra Giocondo incorporated a sunken ditch into his sloping scarp-counterscarp design.
[edit] Additional modifications
Later advances provided additional protection to the scarp and counterscarp defense through the introduction of a stone faced glacis on the slopes. In some instances, the counterscarp may have been protected further with paling fencing to make it more difficult for attackers to invade.
Another sunken space behind the glacis was added to offer a hiding place for defenders. Counterscarp galleries were also introduced as a place for defenders to counterattack.
This type of fortress configuration was used for several centuries, until advances in weaponry required a new solutions.
[edit] Related articles
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.