Blue roof
A blue roof is a roof designed for the retention of rainwater above the waterproofing element of the roof. This is as opposed to more conventional roofs which allow for rainwater to drain from the roof. Blue roofs are typically flat, without any fall, with control devices regulate drainage outlets that enable water to be retained or drained.
The SuDS Manual published by CIRIA in 2015 suggests that a blue roof is: ‘A roof construction that stores water, can include open water surfaces, storage within or beneath a porous media or modular surface or below a raised decking surface or cover.’
Some of the reasons for incorporating a blue roof into a building, include:
- As a form of Sustainable Urban Drainage System (SuDS) to try and alleviate urban flooding caused by stormwater run-off.
- In areas of urban density, the space created by a blue roof can avoid having to provide attenuation for rainwater at ground level.
- Rainwater harvesting for use, independent from, or supplemental to the mains water supply, such as wc flushing or green roof irrigation
- Cooling solar panels, or reducing load on mechanical refrigeration or cooling equipment.
- For recreational purposes, such as rooftop swimming pools or water features.
Unlike some other forms of SuDS, blue roofs make use of spaces that might otherwise be redundant without extending beyond the footprint of the building or into ground space which, depending on the density of the location, may be expensive.
To ensure safety, there must be careful estimation of the flow restriction, which calculates the peak rates of run-off and the water depth that will be formed on the roof surface. This informs the design of the safety overflows, the preventative maintenance programme, and the design and construction of the waterproofing layer.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Blue infrastructure.
- Blue space.
- Brown roof.
- Cold roof.
- Condensation in buildings.
- Domestic roofs.
- Flat roof.
- Flat roof defects.
- Green roof.
- Groundwater control in urban areas.
- Interstitial condensation.
- Living Roofs and Walls, from policy to practice.
- Rain garden.
- Rainwater harvesting.
- Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems.
- Twickenham Studio - London's world-renowned film studio transformed.
- Warm roof.
Featured articles and news
Key points for construction at a glance with industry reactions.
Functionality, visibility and sustainability
The simpler approach to specification.
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
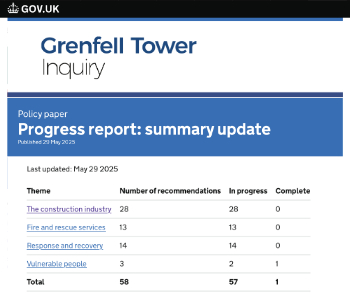
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.