Vacuum Insulated Glazing VIG
Vacuum glazing is similar to double glazing, but the cavity between the panes is a vacuum. The main advantage of vacuum glazing is that it not only performs well but has only a small cavity, which means the glazed units are thin and light in comparison to standard double glazed units.
This type of unit is often the favoured option for historic buildings because vacuum units can be installed as individual panes between the transom and mullions of traditional timber frame windows. The thickness of a vacuum sealed units can be a low as 6mm, which is less than half the thickness of traditional double glazed units (around 20mm) which means in some cases they can even be installed within existing or refurbished timber frames. The performance of such windows can be from around 1.0 W/M2. K down to 0.5 W/M2.K, which is lower than the 1.2 to 3.7 W/(m²K) of standard double glazed units.
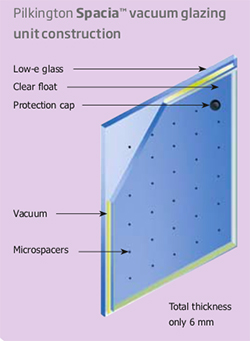
The cost of a vacuum glazed units is likely to be higher than standard double glazed units because of the precision nature of their design and manufacture. The natural effect of having a vacuum between the glazing panes is that the panes want to pull together, they are prevented from doing so through the insertion of tiny micro-spacers, less than a 1mm in diameter laid in a regular grid between the panes. These micro spacers are transparent and can often barely be seen.
The concept for vacuum glazing itself was developed as a proof of concept in the 1990's at the University of Sydney with initial commercialisation by Nippon Sheet Glass, Japan, in 1996. Pilkington glass consider their own SpaciaTM glazed unit to have been the world's first commercially available vacuum glazing, with sales starting a year later in 1997.
Pilkington Spacia™ is one example of a vacuum sealed product and available from Pilkington. It offers the thermal performance of conventional double glazing in the same thickness as a single glass pane. It balances historic preservation with modern comfort and environmental requirements, with a float glass pane on the inside and a low-emissivity glass pane on the outside, hermetically sealed. A diagram of the how a pane is made-up is given here, courtesy of the Pilkington, for further information visit the website directly by clicking the image.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Conservation rooflights.
- Domestic windows.
- Double glazing.
- Double glazing v triple glazing.
- Glass.
- Glazier.
- Glazing.
- Low-E glass.
- Patent glazing.
- Secondary glazing.
- Security glazing.
- Stained glass.
- Structural glass assembly.
- Suction lifter.
- Tempered glass.
- Triple glazing.
- Types of window.
- Window.
- Window frame.
Featured articles and news
Latest Build UK Building Safety Regime explainer published
Key elements in one short, now updated document.
UKGBC launch the UK Climate Resilience Roadmap
First guidance of its kind on direct climate impacts for the built environment and how it can adapt.
CLC Health, Safety and Wellbeing Strategy 2025
Launched by the Minister for Industry to look at fatalities on site, improving mental health and other issues.
One of the most impressive Victorian architects. Book review.
Common Assessment Standard now with building safety
New CAS update now includes mandatory building safety questions.
RTPI leader to become new CIOB Chief Executive Officer
Dr Victoria Hills MRTPI, FICE to take over after Caroline Gumble’s departure.
Social and affordable housing, a long term plan for delivery
The “Delivering a Decade of Renewal for Social and Affordable Housing” strategy sets out future path.
A change to adoptive architecture
Effects of global weather warming on architectural detailing, material choice and human interaction.
The proposed publicly owned and backed subsidiary of Homes England, to facilitate new homes.
How big is the problem and what can we do to mitigate the effects?
Overheating guidance and tools for building designers
A number of cool guides to help with the heat.
The UK's Modern Industrial Strategy: A 10 year plan
Previous consultation criticism, current key elements and general support with some persisting reservations.
Building Safety Regulator reforms
New roles, new staff and a new fast track service pave the way for a single construction regulator.
Architectural Technologist CPDs and Communications
CIAT CPD… and how you can do it!
Cooling centres and cool spaces
Managing extreme heat in cities by directing the public to places for heat stress relief and water sources.
Winter gardens: A brief history and warm variations
Extending the season with glass in different forms and terms.
Restoring Great Yarmouth's Winter Gardens
Transforming one of the least sustainable constructions imaginable.