Retractable bridge

|
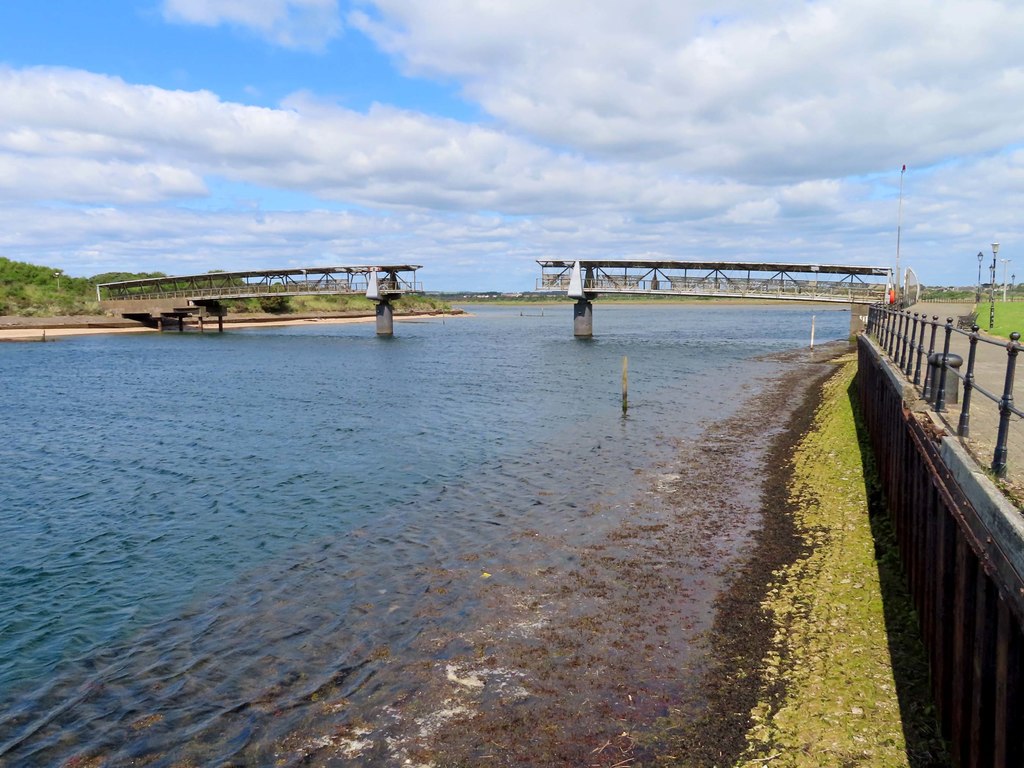
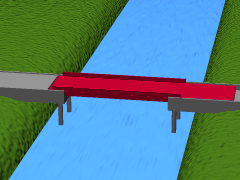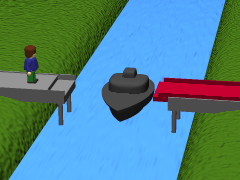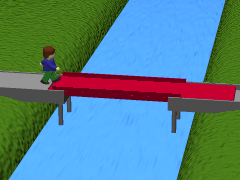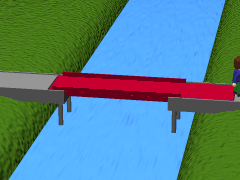
| Retractable bridges, such as this one located in Demerara Harbour, are popular in Guyana. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Bridges are a common feature of the built environment and one of the key elements of civil engineering. The basic principles of bridge design are dependent on the load-bearing structure. These are generally beam, arch or suspension structures.
Some bridges are also defined by other characteristics, for example a movable bridge is defined by its functionality. These bridges are designed in a way that allows them to accommodate different situations and different types of traffic.
One kind of movable bridge is a retractable bridge or thrust bridge. Modern versions of rolling bridges may be referred to as retractable bridges.
[edit] Retractable bridges
This type of movable bridge can slide to an open position to provide clearance for waterway traffic. There are several methods that can be used to perform this retraction function.
[edit] Retractile
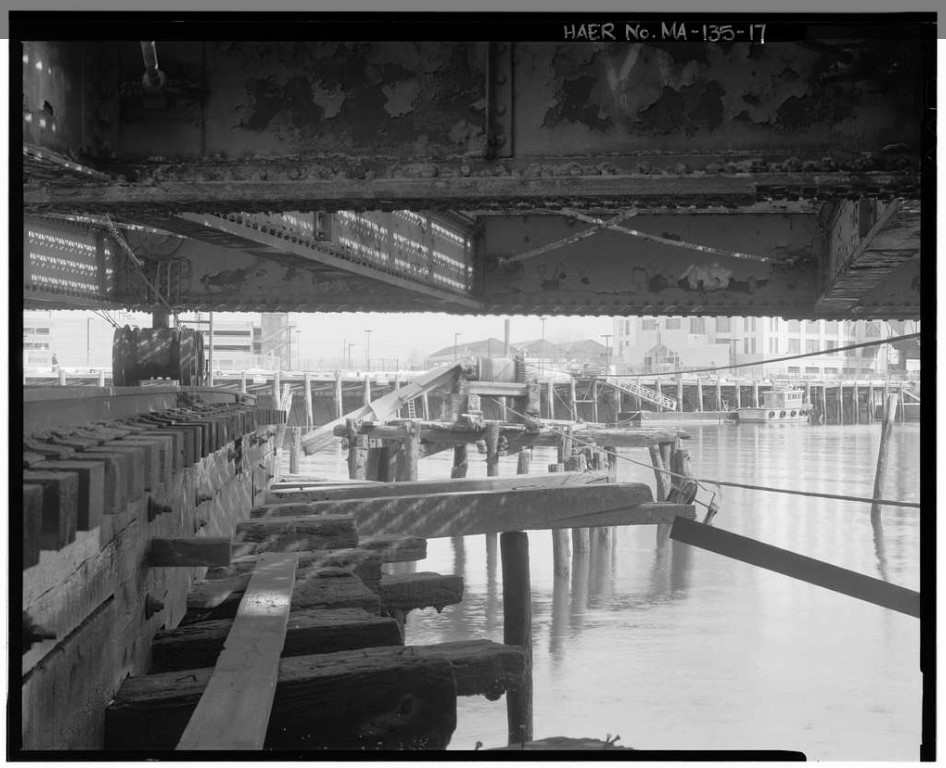
A classic retractile bridge is one in which the span is pulled away on rails. It is believed that this type of retractile bridge was invented by Thomas Willis Pratt in the 1860s.
The Summer Street Bridge in Boston, Massachusetts, is a retractile bridge that was built in 1899. The bridge was the site of a major traffic accident in 1916. It is still standing over the Reserved Channel, but the retractile function was decommissioned in 1970.
[edit] Floating
Some retractable bridges in the Netherlands are floating bridges known vlotbrugs. These floating bridges are positioned across canals, and when necessary, the road is retracted into structures that have been built into the canal banks.
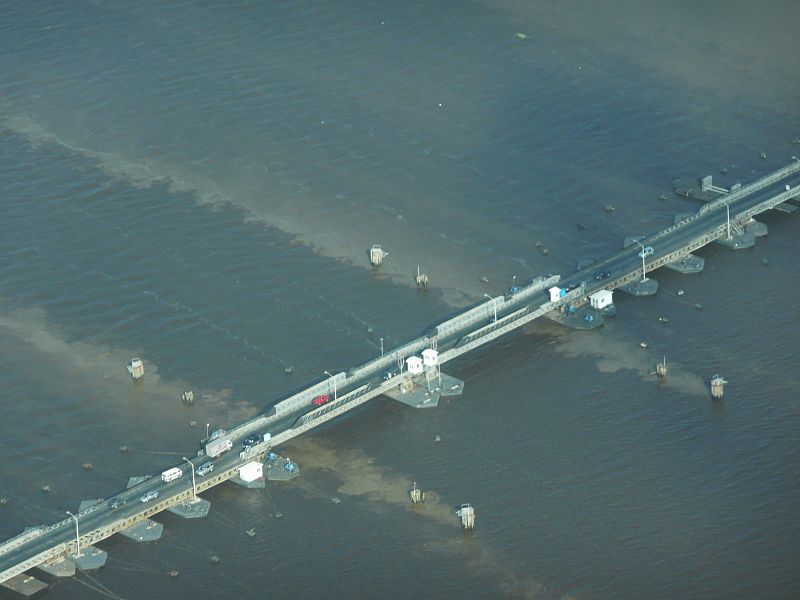
An alternative example of a floating retractable bridge is the Hood Canal pontoon bridge in Puget Sound, Washington. When the bridge needs to be opened for waterway traffic, a section of the floating roadway is hydraulically raised up so the retracting portion can slide underneath it.
[edit] History
Because the movement of retractable bridges can require a large dedicated area to accommodate its footprint, they are no longer commonly used. However, their origins date back to medieval times.
|
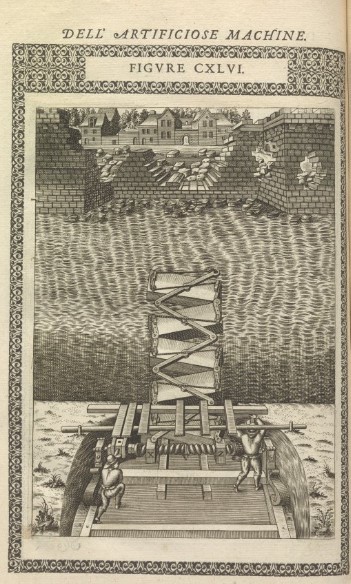
This copper-plate engraving from ‘Le diverse et artificiose machine’ (The various and ingenious machines) illustrates the concept proposed by Agostino Ramelli (1531-c 1600). |
One early example was created in 1588 by Agostino Ramelli. The Italian engineer gained favour with King Henry III of France after providing a strategic method of military engineering that resulted in the breach of enemy defences. In his book of engineering designs, Ramelli proposed a retractable bridge for crossing a moat.
[edit] Noteworthy retractable bridges
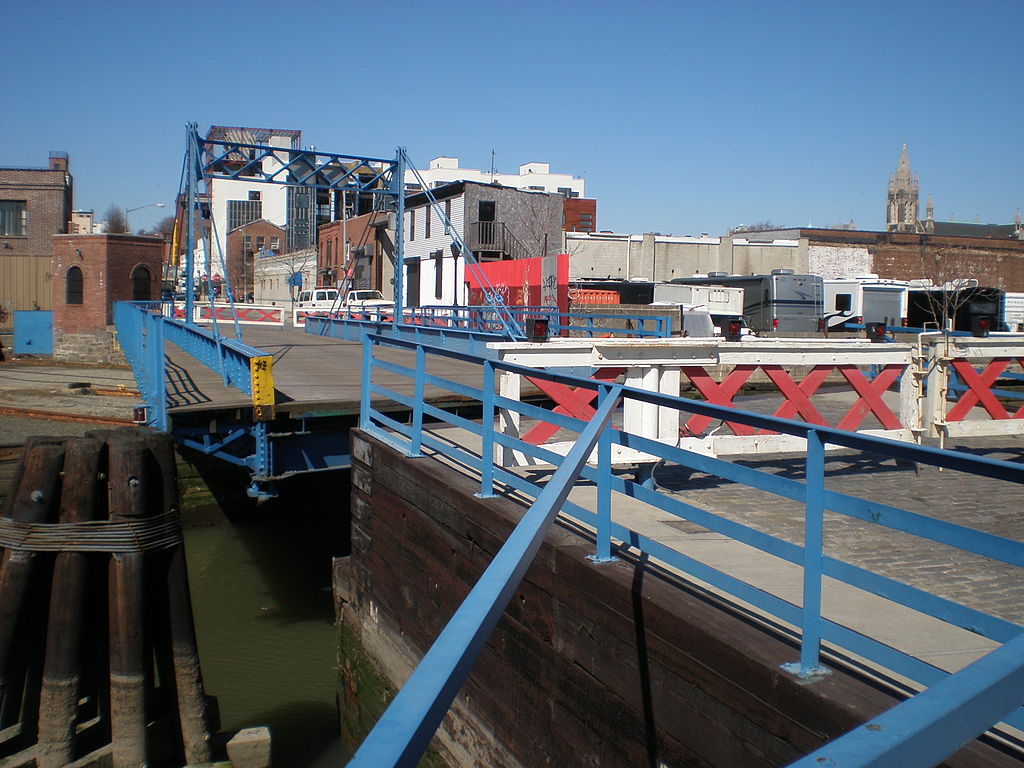
Built in 1889, the Carroll Street Bridge in Brooklyn, New York is one of the oldest retractable bridges in the United States. It is one of New York City’s last bridges built with wooden planks to allow automobiles to cross (although there are strict height and weight restrictions). It was designated as a New York landmark in 1987.
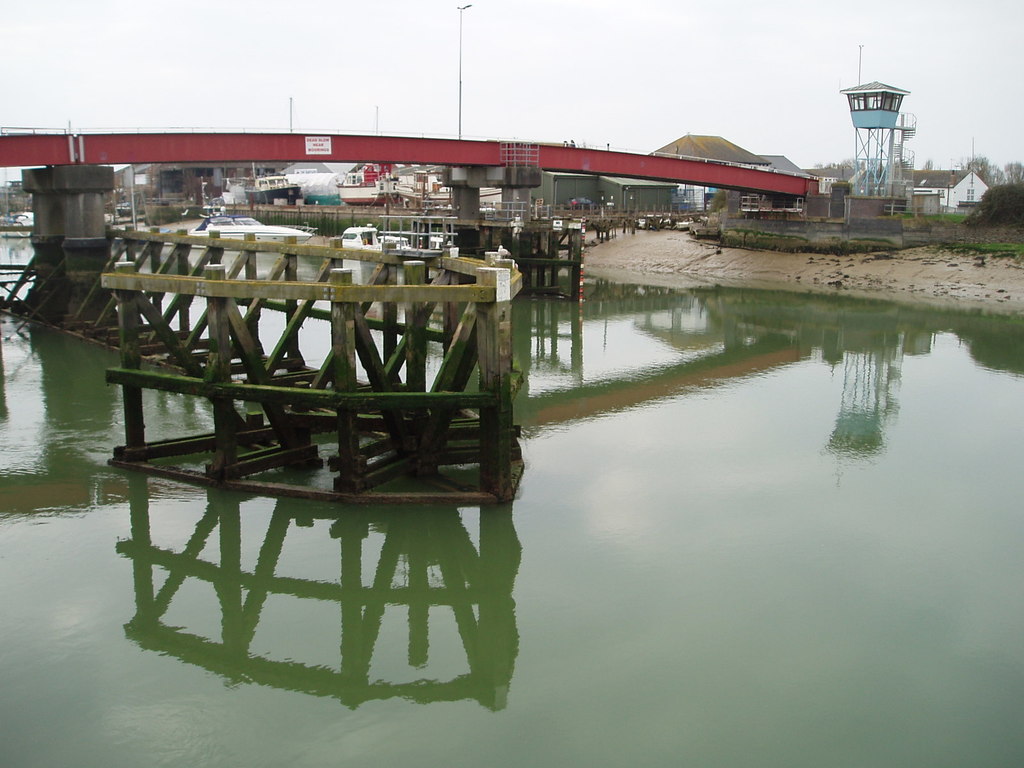
The Littlehampton ferry footbridge was built in the 1980s. Known by locals as The Red Bridge, this retractable pedestrian bridge over the River Arun in Sussex is made from concrete, brick and steel. Powered by electricity, the structure retracts to accommodate ships that require access to adjacent industrial areas.
The Littlehampton retractable bridge underwent a refurbishment in April 2021. The project included repainting the bridge - in its trademark red colour - with a product designed to reduce maintenance costs.
|
The Red Bridge in Littlehampton, Sussex. |
The Bridge of Scottish Invention is a retractable footbridge situated over the River Irvine. It was built to provide access to The Big Idea science centre in North Ayrshire, Scotland. The museum closed in 2003 after just three years in operation. However, the bridge still retracts to allow tall ships to pass through.
The Bridge of Scottish Invention is one of the closest bridges to the open sea of any movable bridge across a river in Great Britain.
|
The Bridge of Scottish Invention in North Ayrshire, Scotland. |
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
IHBC NewsBlog
RICHeS Research Infrastructure offers ‘Full Access Fund Call’
RICHesS offers a ‘Help’ webinar on 11 March
Latest IHBC Issue of Context features Roofing
Articles range from slate to pitched roofs, and carbon impact to solar generation to roofscapes.
Three reasons not to demolish Edinburgh’s Argyle House
Should 'Edinburgh's ugliest building' be saved?
IHBC’s 2025 Parliamentary Briefing...from Crafts in Crisis to Rubbish Retrofit
IHBC launches research-led ‘5 Commitments to Help Heritage Skills in Conservation’
How RDSAP 10.2 impacts EPC assessments in traditional buildings
Energy performance certificates (EPCs) tell us how energy efficient our buildings are, but the way these certificates are generated has changed.
700-year-old church tower suspended 45ft
The London church is part of a 'never seen before feat of engineering'.
The historic Old War Office (OWO) has undergone a remarkable transformation
The Grade II* listed neo-Baroque landmark in central London is an example of adaptive reuse in architecture, where heritage meets modern sophistication.
West Midlands Heritage Careers Fair 2025
Join the West Midlands Historic Buildings Trust on 13 October 2025, from 10.00am.
Former carpark and shopping centre to be transformed into new homes
Transformation to be a UK first.
Canada is losing its churches…
Can communities afford to let that happen?