Pulley
|
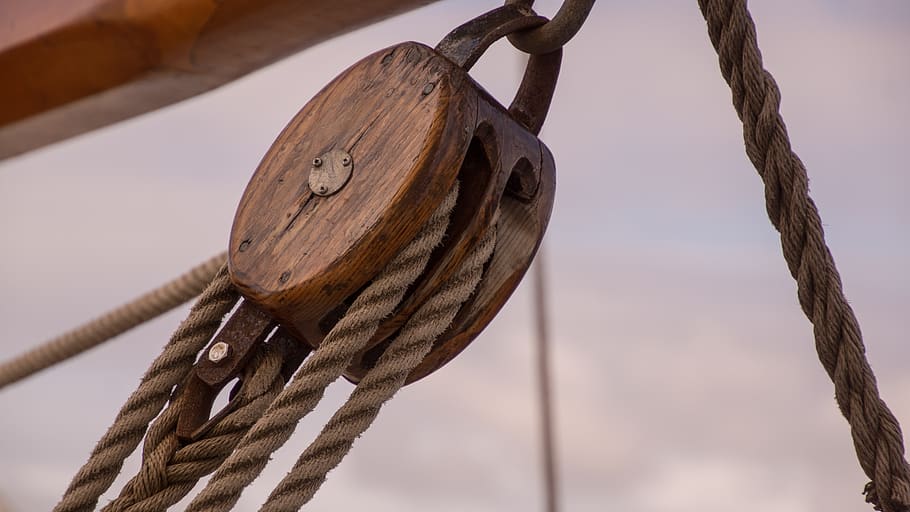
This photograph shows a rope and pulley (or block and tackle) system. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
A pulley is a type of wheel system is used with an axle to support the movement of some type of load.
[edit] History
The earliest recorded existence of pulley systems appeared in Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and Greece where block and tackle configurations were commonly used to move heavy objects.
During the Renaissance, this system was included by scientists in their list of six simple machines. According to Galileo Galilei, the simple machines “do not create energy, only transform it.” In addition to the pulley, these machines included:
- Lever
- Wheel and axle
- Inclined plane
- Wedge
- Screw
The six simple machines often served as the basis for more complex machines.
[edit] Types of pulleys
There are several types of pulley:
- Fixed. A fixed pulley has an axle mounted in bearings attached to a supporting structure.
- Movable. A movable pulley is made up of an axle in a movable block. A single movable pulley can lift more than a single fixed pulley.
- Compound. This combination of fixed and movable pulleys is also known as rope and pulley or block and tackle. When a fixed pulley is combined with a movable pulley or another fixed pulley, it can achieve more ambitious mechanical goals.
[edit] Rope and pulley
When used in combination with a frame or shell (sometimes referred to as a block), the freely rotating movable pulley (or set of pulleys) may be referred to as a sheave. The pulley or sheave may have indentations or grooves around its circumference to accommodate a drive element (sometimes referred to as a tackle) in the form of a continuous cable, belt, rope or chain. The tackle transmits tension to move a load.
This combination of rope and pulley can be part of a simple system that is used to lift items or change the direction of their motion. With the aid of a block and tackle system, it is possible to lift heavy loads by the application of a relatively small amount of force.
There are different types of rope and pulley configurations. The variations are based on the tackle configuration. Increasing the number of pulleys and falls of tackle increases the load that can be moved. Pulleys can be incorporated into common items such as curtains and sliding doors or lifting equipment such as fire ladders or power–driven industrial trucks and so on.
[edit] LOLER and rope and pulley systems
The Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) place legal duties and responsibilities on those who own, operate or have control over lifting equipment. Rope and pulley systems are one type of lifting equipment covered by the regulations.
LOLER was created under the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974, and came into force in 1998, replacing several preceding pieces of legislation which had previously regulated the use of lifting equipment. LOLER defines lifting equipment as ‘work equipment for lifting or lowering loads and includes its attachments used for anchoring, fixing or supporting it.’
The regulations require:
- That lifting equipment is strong and stable enough for safe use.
- Equipment is marked to indicate safe working loads.
- Equipment is positioned and installed so as to minimise risks.
- A competent person plans, organises and performs the safe use of the equipment.
- Equipment is subject to ongoing thorough examination and inspection.
LOLER may not apply where a lift is not used by people at work (such as a lift in a shop used by customers). However, Section 3 of the Health and Safety at Work Act imposes general responsibilities for the safety of users.
LOLER requires that lifts are thoroughly examined by a competent person at least every six months or, in the case of goods-only lifts, every 12 months. Insurance companies will generally request that a third party independent inspector carries out the inspections. The minimum requirements are:
- Every six months for lifting equipment used for lifting/lowering persons.
- Every six months for lifting accessories.
- Every 12 months for all other lifting equipment not falling into either of the categories above.
[edit] Belt and pulley
Another use of the pulley is the belt and pulley system. This system uses a pulley in conjunction with a belt drive to direct power from one place to another. The belt and pulley system can also control the speed of the motion.
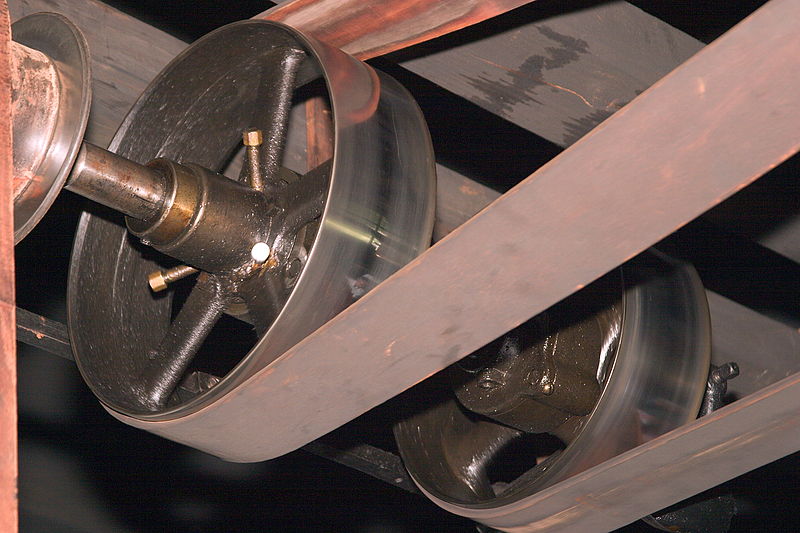
|
This photograph shows a belt and pulley system. |
This configuration consists of two or more pulleys used in conjunction with a belt. The necessary contact pressure between the belt and pulleys is ensured by appropriate tightening of the belt. This may be achieved by means of a tensioning roller or another pulley.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.