Certainty
Emissions Gap Report 2019 published by the UN Environment Programme defines uncertainty as: ‘A cognitive state of incomplete knowledge that can result from a lack of information or from disagreement about what is known or even knowable. It may have many types of sources, from imprecision in the data to ambiguously defined concepts or terminology, or uncertain projections of human behaviour. Uncertainty can therefore be represented by quantitative measures (for example a probability density function) or by qualitative statements (for example reflecting the judgement of a team of experts).’
Articles on Designing Buildings Wiki relating to types of uncertainty include:
Competence frameworks for the built environment – Core criteria for sustainability competence - Code of practice , Version 3, published by the Edge for the Construction Industry Council in February 2025 defines the following types of uncertainty:
- Deep uncertainty: A situation of deep uncertainty exists when experts or stakeholders do not know or cannot agree on: (1) appropriate conceptual models that describe relationships among key driving forces in a system; (2) the probability distributions used to represent uncertainty about key variables and parameters; and/or (3) how to weigh and value desirable alternative outcomes.
- Interpolation uncertainty: Uncertainty arising from a statistical or physical model-based interpolation of a field between available estimates to create a more spatio-temporally complete estimate.
- Sampling uncertainty: Uncertainty arising from incomplete or uneven availability of measurements in either space or time or both.
- Trend estimates uncertainty: Uncertainty arising from data fitting to a time-series with potential non-linear and autorogressive character.
NB Guide to developing the project business case, Better business cases: for better outcomes, published by HM Treasury in 2018, suggests that uncertainty: ‘Is unmeasured risk where known risks are not yet well enough understood to be estimated in terms of probability or impact and where not all risks may be identified and quantified.’
Anticipate, react, recover; Resilient infrastructure systems, published by the National Infrastructure Commission in May 2020, defines uncertainty as: ‘Limited and unknowable knowledge about future, past, or current events and conditions. Uncertainty includes natural variability (aleatory uncertainty), knowledge gaps (epistemic uncertainty), ambiguous meanings (semantic uncertainty), unknown unknowns (ontological uncertainty), and subjectivity.’
AR5 Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability, Glossary, published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) defines uncertainty as: ‘A state of incomplete knowledge that can result from a lack of information or from disagreement about what is known or even knowable. It may have many types of sources, from imprecision in the data to ambiguously defined concepts or terminology, or uncertain projections of human behavior. Uncertainty can therefore be represented by quantitative measures (e.g., a probability density function) or by qualitative statements (e.g., reflecting the judgment of a team of experts)’
Cost prediction, Professional Statement, 1st edition, published in November 2020 by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS), defines uncertainty as: ‘A lack of complete certainty. In uncertainty, the outcome of any event is entirely unknown, and it cannot be measured or guessed; there is no background information on the event. Uncertainty is not an unknown risk.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
First aid in the modern workplace with St John Ambulance.
Ireland's National Residential Retrofit Plan
Staged initiatives introduced step by step.
Solar panels, pitched roofs and risk of fire spread
60% increase in solar panel fires prompts tests and installation warnings.
Modernising heat networks with Heat interface unit
Why HIUs hold the key to efficiency upgrades.
Reflecting on the work of the CIOB Academy
Looking back on 2025 and where it's going next.
Procurement in construction: Knowledge hub
Brief, overview, key articles and over 1000 more covering procurement.
Sir John Betjeman’s love of Victorian church architecture.
Exchange for Change for UK deposit return scheme
The UK Deposit Management Organisation established to deliver Deposit Return Scheme unveils trading name.
A guide to integrating heat pumps
As the Future Homes Standard approaches Future Homes Hub publishes hints and tips for Architects and Architectural Technologists.
BSR as a standalone body; statements, key roles, context
Statements from key figures in key and changing roles.
ECA launches Welsh Election Manifesto
ECA calls on political parties at 100 day milestone to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
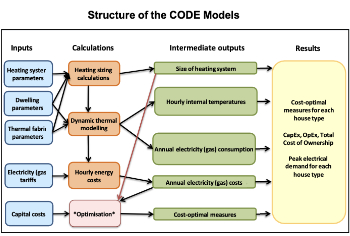
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.




















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.