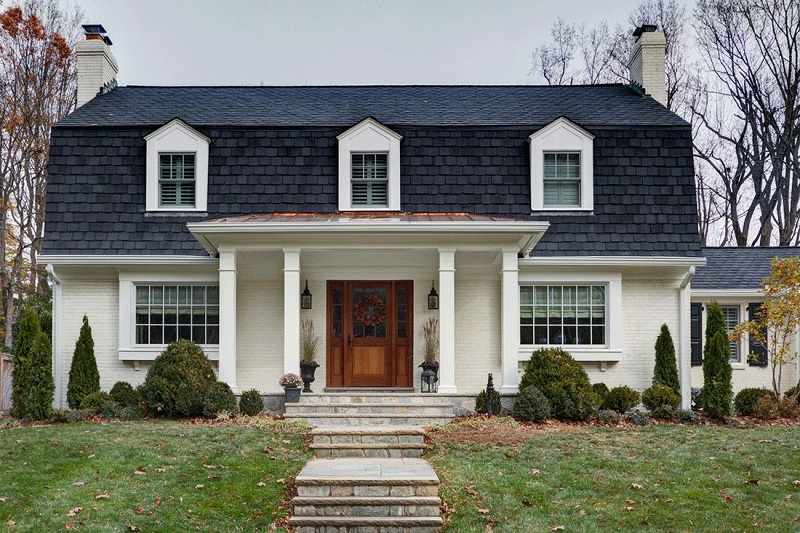
Mansard roof
A mansard roof, also known as a French or curb roof, is a roof characterised by that fact that each of its four sides has two pitches, the lower pitches being steeper than the upper pitches. It is similar to a gambrel roof but differs in that it displays the same profile on all sides (whereas a gambrel roof has vertical gables at either end). The lower slope is commonly fitted with dormer windows.
Mansard roofs allow for increased space beneath their steeper sides. They maximise headroom inside the upper storey of the building whilst lowering, what would if it were simply-pitched, be a very tall roof. The mansard form can also help water runoff, as the pitch increases towards the eaves, where the runoff is likely to be at its greatest.
When viewed from near the building at ground level, the upper slope is often not visible.
The commonly-attributed earliest example of a mansard roof is the Louvre, designed by Pierre Lescot around 1550. It was popularised in the French Baroque period by Francois Mansart and became widely used during the Second French Empire (1852-1870) as well as in the United States and Europe. One of the factors attributable for its popularity in France was that houses were taxed by height or the number of storeys below the roof. The design of the mansard enabled the creation of an additional floor without having to pay additional tax.
NB The National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF), published by the Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government in December 2024, defines a mansard roof as: ‘A type of roof that is characterised by two slopes, the lower steep and the upper shallow. It is generally regarded as a suitable type of roof extension for buildings which are part of a terrace of at least three buildings and at least two stories tall, with a parapet running the entire length of the front façade (reference: Create Streets, 2021, Living Tradition).’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
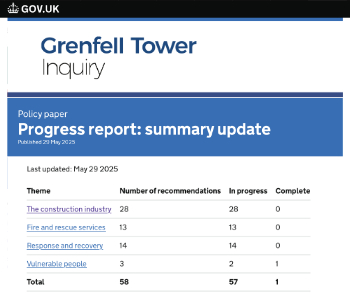
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.
























Comments
I love this design!!! I have a home with a mansard roof and I am trying to renovate the front. I am wondering if you know the dimensions of the two windows on each side of the door?