The world’s fastest mode of transport could soon be here
Imagine if it only took a day for products to travel over land from China to Germany.
It could soon be a reality, if Russia goes ahead with a plan to introduce a new fast-speed pipeline called the Hyperloop. Much as oil and gas travel through pipes, cargo and passengers may soon find themselves shooting through pneumatic tubes at speeds of up to 760 miles per hour.
Tech entrepreneur Elon Musk once envisioned a tube transportation project that could move passengers and cargo from San Francisco to Los Angeles in 30 minutes. Two companies – Hyperloop One (formerly Hyperloop Technologies) and Hyperloop Transportation Technologies (HTT) – are now exploring Musk’s idea with a view to building the first transport-ready tube by 2020.
According to the chief executive officer of Hyperloop One, feasibility studies have been launched not only in Russia but also in the United Arab Emirates, Finland, the United Kingdom and the United States.
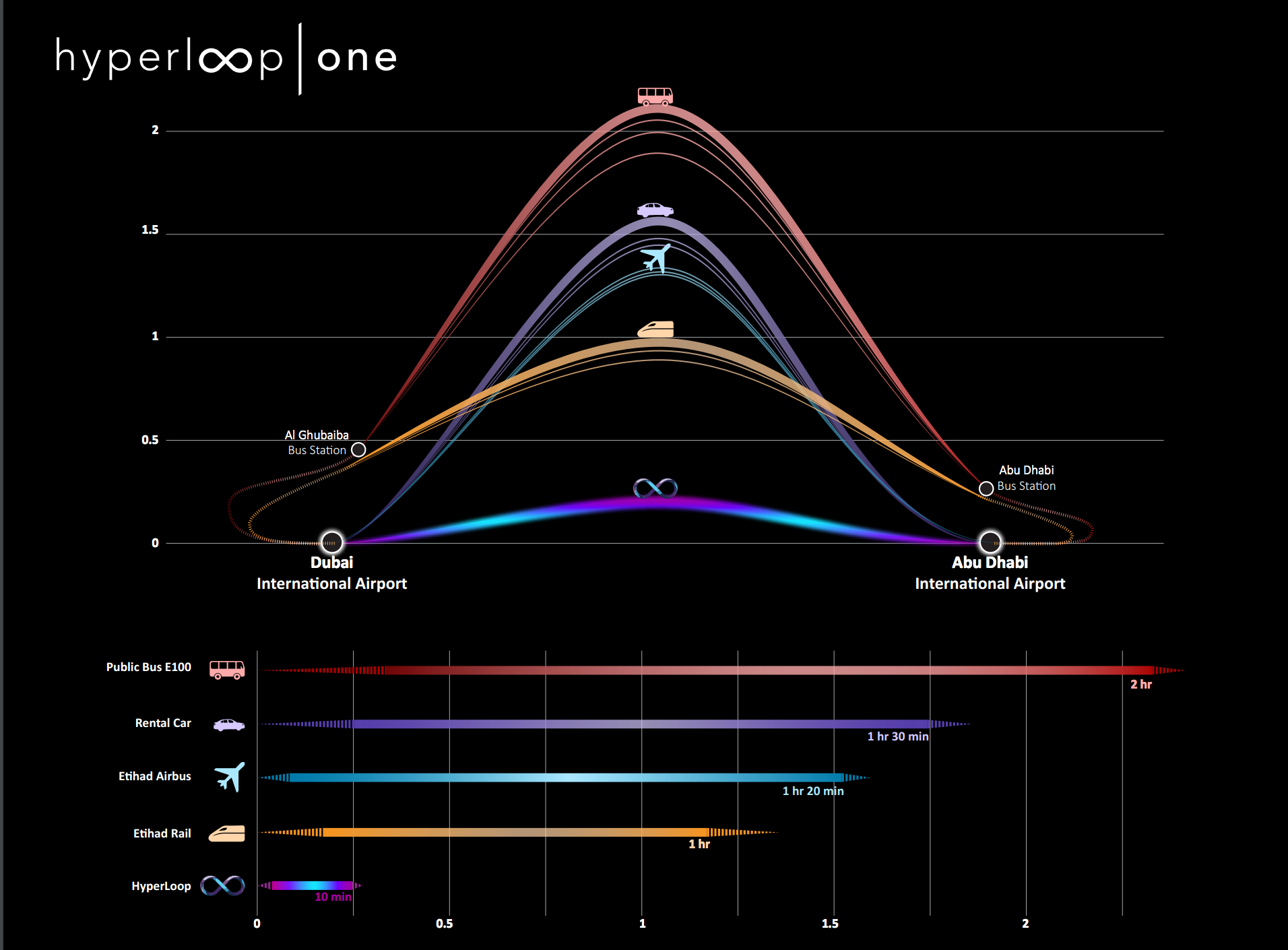
Hyperloop One has joined forces with the city of Moscow and Summa Group, a local investment and construction conglomerate, to bring the vacuum tube to Russia.
So what are the benefits?
Air transportation is fast but costly, so most cargo is shipped by sea. To travel by sea between Asia and Europe can take around 30 days – and that’s without considering overland transport to and from the ports. Rail transportation takes nearly half that.
The southern rail route between China and Russia is 6,213 miles long and takes 12 days, while an 8,077-mile northern rail route through Russia takes 16 days. Can the Hyperloop ultimately provide the quickest transportation option, at affordable cost?
Construction costs are important to consider. Building and operating a Hyperloop is estimated to be in a similar range as building and operating high-speed rail infrastructure and trains. The construction cost for high-speed rail lines, such as the Haikou-Sanya line in China and Madrid-Albacete line in Spain, come in at about US$15 million a mile.
Elon Musk suggested that a San Francisco-Los Angeles Hyperloop would cost $11.5 million a mile. Hyperloop One estimates the cost of building the vacuum tube to be anywhere between $5 - 20 million a mile.
However, the cost might be much higher if instead of pressurised air generated by compressors (as proposed by Musk) the more expensive magnetic levitation technology is installed, using powerful electromagnets to lift the train carriages. The 19-mile 'maglev' line in Shanghai has cost $63 million a mile, and a proposed 178-mile track in Japan is expected to cost roughly $250 million a mile.
Earlier in 2017, HTT announced an exclusive deal to licence passive magnetic levitation technology, which would eliminate the need for power stations along the track and could therefore lower operating costs. Also, HTT had filed permits in Kings County, California to build a five-mile test track.
Hyperloop One tested the propulsion mechanism on 11 May 2016 in Nevada. Although the test result can be considered a first proof of concept, the outcome isn’t yet clear as the demonstration focused only on one part of the complex solution.
The race is on. But a project the size of the Transonic Silk Road would require sizeable political and financial support from China. Initial interest seems to exist: CRRC Corp, China’s largest maker of railway equipment, has apparently been in talks for a potential investment in Hyperloop One, according to a Bloomberg report earlier in 2017.
Depending on these developments, the Belt and Road initiative might soon connect Asia and Europe overnight by the Hyperloop, potentially requiring a quick name change from Belt and Road to Belt and Tube.
Written by Wolfgang Lehmacher, Head of Supply Chain and Transport Industries, World Economic Forum
This article was originally published on the Future of Construction Knowledge Sharing Platform and the WEF Agenda Blog.
Have you read?
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Hyperloop in Dubai.
- Hyperloop One.
- The challenges facing Hyperloop One.
- The transport revolution of Hyperloop.
--Future of Construction 14:08, 20 Jun 2017 (BST)
Featured articles and news
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.