Standard hatching styles for drawings
Contents |
[edit] Why is hatching used on drawings?
Hatching styles are patterns used on drawings for the easy identification and location of different types of commonly-used materials, objects and spaces.
Hatching can also be used as a form of shading - for example to indicate shadows.
[edit] How is hatching done?
Historically, hatches were drawn by hand, but the development of transfers, and then drawing software enabled considerable time savings on what was a very repetitive and time consuming task. Today, hatch commands can be used to fill a selected area or material with a standard hatching pattern almost instantly. For example, a bathroom can be tile-filled by selecting the relevant hatching style to indicate tiles, and applying it to the whole tiled area of the drawing. The use of parametric software allows common attributes to be attached to a number of similar elements, so that, for example, all tiled areas in a building can be hatched in one command, and changes can be applied throughout.
[edit] Examples of common hatching patterns
Some of the most common hatching styles are set out below. To make this list more comprehensive, click 'Edit this article' at the top of the page and add more.

|
Aggregate |

|
Blockwork wall |
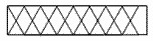
|
Blockwork |
|
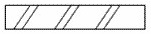
Brickwork |

|
English bond wall |

|
Garden bond wall |
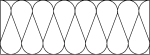
|
Insulation |

|
Concrete |

|
Finewood |

|
Hardwood |

|
Plywood |

|
Glass |

|
Gravel |
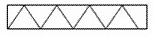
|
Hardcore |
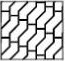
|
Paving |

|
Rubble |

|
Sand |

|
Stone |
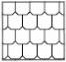
|
Shingles |
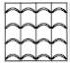
|
Roofing tiles |
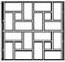
|
Floor tiles |
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.





















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.
Please add more hatching styles to this article to make it more comprehensive.