Spiral stairs and helical stairs
Spiral and helical staircases can create a sense of light within properties, they can take up less space than traditional stairs, and can create a focal point to a design. They are often available as pre-fabricated kits.
Approved document K, Protection from falling, collision and impact, gives the following definitions.
- A spiral stair is a stair in a helix around a central column.
- A helical stair is a stair in a helix around a central void.
The approved document requires that spiral stairs and helical stairs are designed in accordance with BS 5395-2 Stairs, ladders and walkways. Code of practice for the design of helical and spiral stairs [1984 + AMD 6076, Corrigenda July 2008, C2, C3]. It gives recommendations for the design of internal and external helical and spiral stairs and gives guidance on the geometry of helical and spiral stairs, including:
- Alternative materials, components and methods of design and construction.
- Materials.
- Design.
- Fire protection and means of escape.
- Load tests.
- Design geometry.
- Typical layouts for stairs.
- Relationship between rise and going.
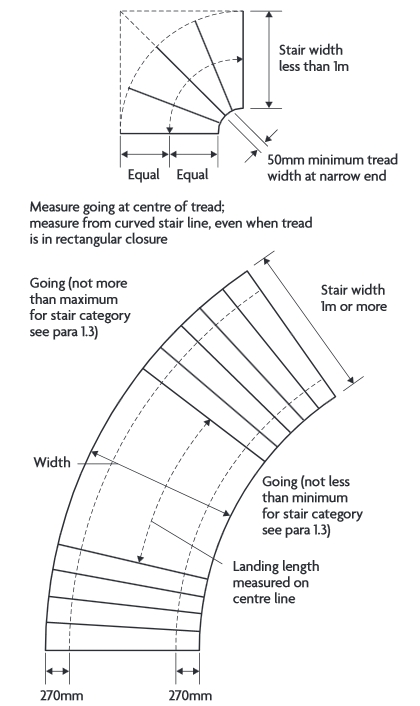
- Measurement of clear width and goings.
- Landings.
- Maximum gap between column and tread.
- Calculation of going.
- Calculation of clear headroom.
- Structural materials.
- Sizes of stairs.
Helical and spiral stairs involve the use of tapered treads. A tapered tread is a step in which the going (the depth from front to back of a tread, less any overlap with the next tread above) reduces from one side to the other. Approved document K requires that consecutive tapered treads, should use the same going. If a stair consists of straight and tapered treads, the going of the tapered treads should not be less than the going of the straight treads.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.