Spiral stairs and helical stairs
Spiral and helical staircases can create a sense of light within properties, they can take up less space than traditional stairs, and can create a focal point to a design. They are often available as pre-fabricated kits.
Approved document K, Protection from falling, collision and impact, gives the following definitions.
- A spiral stair is a stair in a helix around a central column.
- A helical stair is a stair in a helix around a central void.
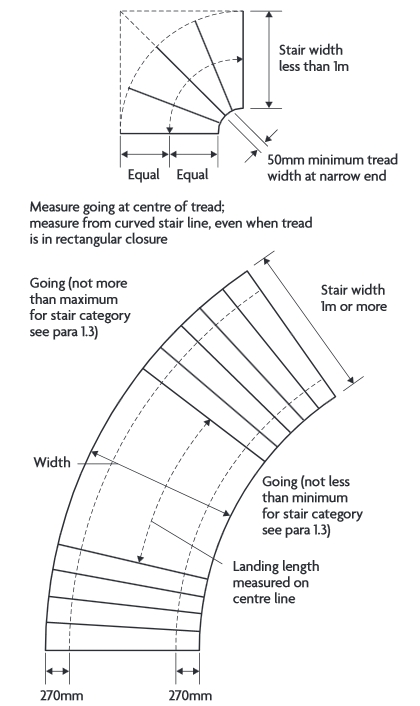
The approved document requires that spiral stairs and helical stairs are designed in accordance with BS 5395-2 Stairs, ladders and walkways. Code of practice for the design of helical and spiral stairs [1984 + AMD 6076, Corrigenda July 2008, C2, C3]. It gives recommendations for the design of internal and external helical and spiral stairs and gives guidance on the geometry of helical and spiral stairs, including:
- Alternative materials, components and methods of design and construction.
- Materials.
- Design.
- Fire protection and means of escape.
- Load tests.
- Design geometry.
- Typical layouts for stairs.
- Relationship between rise and going.
- Measurement of clear width and goings.
- Landings.
- Maximum gap between column and tread.
- Calculation of going.
- Calculation of clear headroom.
- Structural materials.
- Sizes of stairs.
Helical and spiral stairs involve the use of tapered treads. A tapered tread is a step in which the going (the depth from front to back of a tread, less any overlap with the next tread above) reduces from one side to the other. Approved document K requires that consecutive tapered treads, should use the same going. If a stair consists of straight and tapered treads, the going of the tapered treads should not be less than the going of the straight treads.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherit assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.