How 5 cities are working to wipe out diabetes
[Image: REUTERS/Mario Anzuoni]
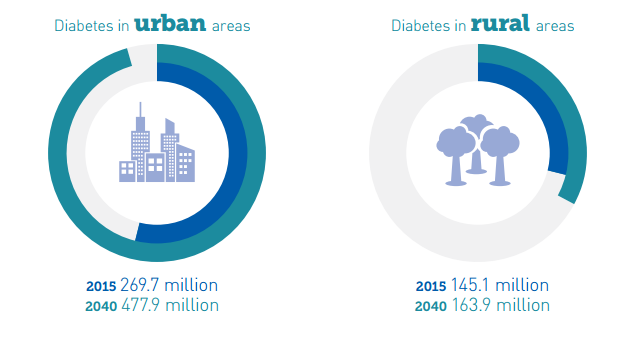
By 2050, two thirds of the world’s population will be city dwellers, the result of a trend towards rapid urbanisation that presents both new opportunities and challenges.
On the one hand, people are drawn to the social and economic possibilities of an urban life, which also brings them closer to health services. On the other hand, certain aspects of city lifestyles are contributing to new and fast-moving public health challenges on an unprecedented scale. Over the next 25 years, the number of people with diabetes will be upwards of half a billion. Three in four of these people will call a city home.
In 2014, recognising the importance of healthy, liveable cities, Novo Nordisk partnered with University College London (UCL) and Steno Diabetes Centre on the Cities Changing Diabetes programme.
The partnership aims to put urban diabetes at the top of the global healthcare agenda, and firmly in the consciousness of those designing and managing the cities of the future. We are working to provide a credible, international understanding of the problem and in turn provide a blueprint for actions that improve individual and public health.
Research led by UCL has already begun to shed light on the challenge and helps us understand what makes city dwellers vulnerable to diabetes. Findings from partner cities Mexico City, Houston, Shanghai, Tianjin and Copenhagen show, for the first time, the significant role played by social and cultural factors in diabetes risk factors.
The factors identified include time pressure, financial constraints, cultural food traditions and shifting perceptions of normal body size. Although they may manifest themselves differently, social and cultural factors are shared by cities around the world and therefore provide a basis for diabetes prevention and management strategies.
If anyone is best placed and motivated to take on board these lessons and rise to the challenge, it is the mayors of some of the world’s largest cities. They are closer to their citizens; they have a clear incentive in ensuring that their cities become more liveable and that their citizens are given the best opportunities to remain healthy and productive. Already we are seeing city leaders responding to the research findings and taking action.
In Copenhagen, research identified hard-to-reach populations at high risk within specific districts of the city. Recognising that reaching these individuals requires a multi-sector response, the municipality has announced plans for a Copenhagen city diabetes specialist centre. The unit will provide a point of care for vulnerable individuals and will draw upon health, employment, housing and peer support resources.
In Houston, the research shattered the myth that disadvantage and diabetes vulnerability go hand-in-hand. A sizeable population of upper-middle class citizens that have never been the target of public health policies were found to be at risk. To address this and other challenges, an alliance of 70+ community and faith-based organisations, healthcare providers and employers have come together to redesign public health policies in Houston along five dimensions:
- Enhance awareness and education to improve diabetes understanding.
- Improve navigation for patients to better use prevention, detection, care and management resources.
- Improve collaboration by providers, insurers and employers to improve patient trust.
- Help people prioritise personal health over other life demands.
- Improve the connections between people at risk of diabetes, with diabetes and caregivers and their community.
In 2016, the movement will grow, as Johannesburg and Vancouver join the programme and start work to better prevent and manage diabetes among their own populations. Whether other cities are part of the programme or simply wish to independently tackle urban diabetes, three clear principles can help them to succeed:
- Create new models for collaboration. This means forging new partnerships that engage all sectors and levels of the community: local government, businesses, schools, non-profits, healthcare providers, grassroots organisations and individuals. This is critical to create policy change that promotes community-wide health and well-being.
- Form peer-to-peer community networks. Since the people most vulnerable to diabetes are often barely reached by the formal healthcare system, we must look beyond it. Peer-to-peer networks can play an important role in changing people’s ability to manage their own health and equipping them to live with diabetes.
- Make health a priority in urban planning. When cities are planned, managed and governed well, they can be engines of prosperity and greater personal well-being. But when this isn’t the case, inequalities, working patterns, lifestyles and cultural norms that cities foster can magnify vulnerabilities to diabetes and other chronic conditions. So leaders in health need to work more closely with those who design and manage cities to ensure urban spaces are thoughtfully optimised for their citizens’ health.
Cities are undoubtedly on the frontline in the fight against global diabetes and it is encouraging to see the emergence of a movement against the condition in the urban setting. Addressing this global challenge will require broader mapping of urban diabetes; continued sharing of lessons learned and collaborative local action. The road to changing diabetes will be a long one, but we will get there – one city at a time.
This article was written by Niels Lund, Vice President, Changing Diabetes, Novo Nordisk
This article was also published on the Future of Construction Knowledge Sharing Platform and the WEF Agenda Blog.
--Future of Construction 16:26, 16 Jun 2017 (BST)
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.