World leaders urged to embrace wind energy
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
On 19 July 2021, representatives of the Global Wind Energy Coalition (GWEC) called on G20 members to show leadership in the climate crisis ahead of COP26 by raising national ambitions and urgently laying out plans for increased wind energy production to replace fossil fuels. GWEC is a member-based organisation that represents the wind energy sector.
[edit] Letter to G20 nations
In an open letter to the G20, 23 CEOs from the GWEC acknowledged that some measures to address climate change have been made. But the letter also pointed out that as of July 2021, net zero pledges from G20 countries still put the world on a 2.4°C global warming pathway, well beyond what is needed to avoid the worst impacts of climate change. According to data collected by the organisation, wind energy and renewable installations are falling short of the trajectory needed to meet international climate goals.
The letter was signed by the leaders of some of the largest wind power companies and associations representing the industry in geographies such as the UK, Brazil, China, Mexico and South Africa. The letter mentioned that the roadmap from the International Energy Agency (IEA) showed that annual wind deployment must quadruple from 93 GW in 2020 to 390 GW in 2030 to meet a net zero by 2050 scenario. Both the IEA and International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) are aligned in the total wind energy capacity required for a net zero scenario, which is compatible with a 1.5°C warming pathway, foreseeing a need for 8,265 GW and 8,100 GW by 2050, respectively.
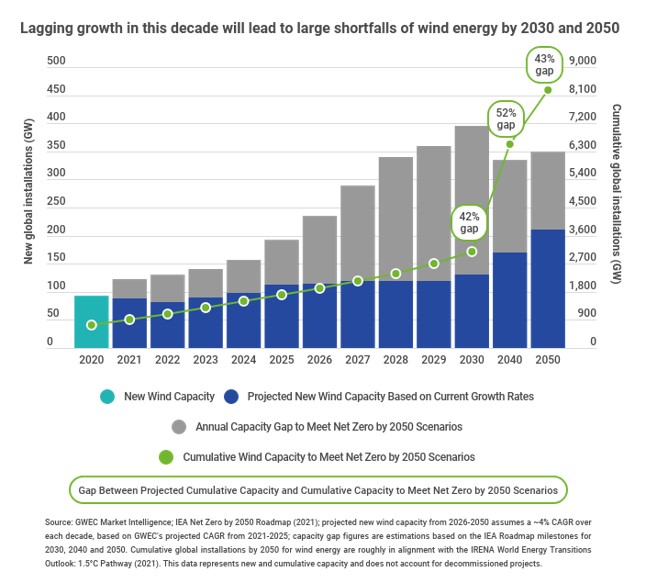
|
If current growth rates for wind energy persist, the letter argues that global wind capacity will fall short of the volumes required for carbon neutrality by 2050, with installation shortfalls of as much as 57%.
[edit] Call to action
To reach the necessary level of deployment, the letter called on G20 nations to:
- Raise ambitions for wind power at national level.
- Implement effective policy and regulatory frameworks for procurement and delivery of renewable energy.
- Commit to clean energy infrastructure plans including grids and transmission.
- Agree effective and credible carbon pricing mechanisms.
- Align national and regional finance flows with benchmarks for a net 1.5°C-compliant pathway.
- Develop cohesive and inclusive policies which dedicate public resources to the shift to a net zero economy.
[edit] Lagging adoption
Since 2000, wind energy has increased production exponentially while reducing some of its costs. It has also helped to create jobs and infrastructure investment. As of 2020, there were approximately 550,000 wind energy workers in China, 260,00 in Brazil, 115,000 in the US and 63,000 in India, according to a global survey by GWEC Market Intelligence.
However, the letter stated that achieving the scale and speed of deployment needed to tap into the employment and infrastructure benefits and achieve net zero ambitions is unrealistic under the present "business as usual" conditions. The signatories feel that global net zero goals will not be realistic unless there is decisive and urgent policy change across the G20 countries.
As of 2021, the top five wind markets in terms of total installed capacity were:
- China – 288 GW
- US – 122 GW
- Germany – 63 GW
- India – 39 GW
- Spain – 27 GW
The letter to the G20 heads of state was also shared with a number of government, energy, finance and institutional leaders, including the leaders of COP26, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), IRENA, IEA, IMF, World Economic Forum (WEF) and a number of development banks.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.

























