Danish energy consumption and climate impact Building Regulations Chapter 11
As of January 1 2023, Chapter 11 of the Danish Building Regulations includes requirements for the overall climate impact of buildings to be calculated according to the Sustainability in construction and construction - Assessment of the environmental quality of buildings - Calculation method (EN 15978:2012).
The new requirements are set out via two elements; a calculation method, which is set out in section 297 and a limiting value, according to that calculation method which is set out in section 297, the regulations require:
- All buildings with a heated floor area of less than 1,000 m2 to document the building's climate impact in accordance with the incorporated calculation method, which is in line with EN 15978:2012.
- All new construction over 1,000 m2 must document the building's climate impact in accordance with the calculation method AND and comply to a given limit.
The requirements introduced have been done so in accordance with the country's National strategy for sustainable construction, which was published in April 2021, with the intention to make the climate impact of buildings more visible and to limit these impacts based on the whole lifecycle of the building. Recommendations are also given in the guidance that life cycle assessments are carried out at the earlier stages of the design phases and continued through all phases of the procurement process to impact decision-making, selection of materials and design approach.
Calculations are required per building, in cases where buildings have differing parts, elements or uses then a weighted average by floor are is to be given. Calculations for groups of smaller buildings can be combined and given as a sample calculation, and this does not automatically mean that the floor areas are aggregated, if each unit is less than 1000m2 then only the calculation is considered as an example or sample. Refurbished or renovation projects, are exempt from the requirements to both calculate and limit the impact, as are extensions, temporary or mobile pavilions and summer houses.
Whilst there are no requirements to use a specific tool for the life cycle assessment, they must be in line with the calculation prerequisites set out in the regulations. The guidance suggests assessments can be carried out with the calculation programme LCAbyg23, developed by BUILD (also in English) as it is in line with the calculation prerequisites.
The standard DS / EN15978:2012 must be followed accordingly;
- Where the period for consideration and modules are defined in subsection 2.
- Where the areas must be calculated as defined in subsection 3.
- Where the building parts to be included appear in subsection 4.
- Where the data basis used appears in subsection 5 and par. 6.
- The lifetimes to be used appear from subsection 7.
- The emission factors that must be used appear in subsection 8.
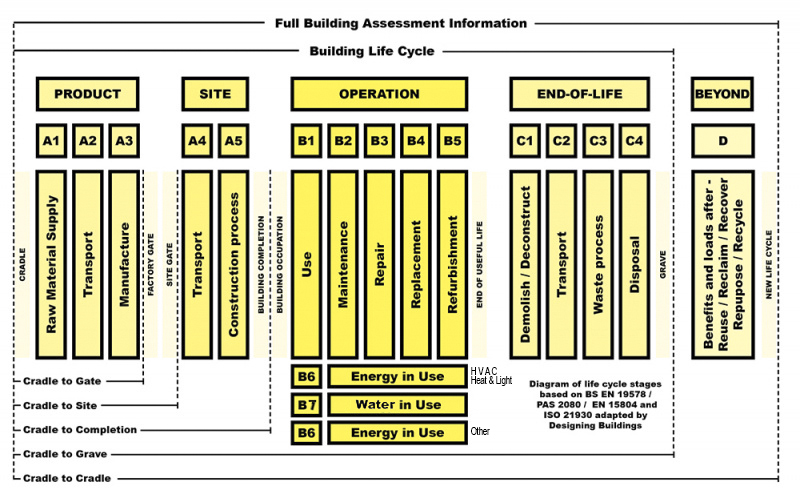
The modules that are required to be included and documented, according to EN 15978:2012 include; product stages A1-A3, operational stages B4 and B6, as well as the end-of-life stages C3 and C4 and stage D, beyond or outside of the project. The other stages A4 and A5, B1-B3, B5 and B7, and C1 and C2 are excluded, whilst stages D that might involve re-use, recovery, recycling and exported energy are to be included in the calculation but are excluded when considering the limiting factor limit for buildings over 1000m2. The calculations are assumed to be over a 50 year lifespan.
The guidance continues in detail to explain further aspects of the regulations including calculation units, floor areas by example, calculations, building parts such as structure, default values, quantities, available databases, composition of materials, individual lifespans, EPDs, emission factors, energy and special circumstances.
For further information visit: https://bygningsreglementet.dk/Tekniske-bestemmelser/11/BRV/Bygningers-klimapåvirkning?Layout=ShowAll - in Dutch
[edit] Related articles of Designing Buildings
- An in-depth look at Environmental Product Declarations EPDs.
- British Standards
- BS EN 15978-1
- Collaboration, standards and their acronyms explained.
- European standards.
- Environmental product declaration EPD
- EN 15804+A1 2012
- EN 15804+A2
- International standards.
- Mandatory environmental impact categories
- Optional environmental impact categories
- Product Environmental Footprint PEF
- Product category rules PCR.
- Sustainable procurement.
- The sustainability of construction works.
Featured articles and news
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.