This is how cities can fight climate change
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Cities are a crucial area for taking action on climate change. By 2050, over two thirds of mankind will live in cities. Cities generate roughly 80% of global GDP and account for more than 60% of all CO2 emissions.
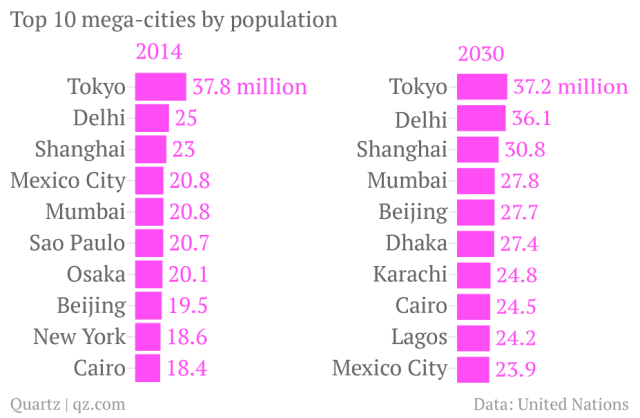
In Asia’s emerging economies, urbanisation is happening at a striking pace. In 2030, seven of the world’s 10 biggest urban centres will be in Asia. More than 55% of China’s population lives in cities today. By 2030, 70% or one billion Chinese will be living in urban areas.
[Image: Quartz]
Clearly, if we want any chance at all to mitigate climate change, we need to develop low-carbon cities. And that puts the spotlight on infrastructure. Infrastructure supports much of what attracts us to cities, including healthcare, education, innovation and culture. Intelligent infrastructure is key to reducing CO2 emissions.
[edit] What does a smart city actually mean?
'Smart cities' is the expression often used in this context. But what exactly is a smart city?
Advances in digitalisation and automation in infrastructure are making significant improvements possible, even through relatively small investments. For example, Siemens have shown how intelligent infrastructure can significantly outperform existing systems – for example, by speeding up traffic by 20%, increasing train capacity by 30%, cutting power consumption in buildings by 30%, or saving up to 40% in the build-out of power grids.
Here are some examples of the positive impact of intelligent technologies.
[Image: REUTERS/Jacky Naegelen]
Transportation is a crucial infrastructure for every city. Paris’ Metro Line 1 is the city’s oldest line and has been operating for 115 years. It transports around 750,000 people per day. Siemens upgraded it to a driverless metro system and increased the capacity by 20%.
[edit] The changing economics of renewables
2015's climate talks in Paris, COP21, conveyed the clear message that our energy mix needs to be diversified. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and energy from waste not only reduce greenhouse gases but are becoming economically attractive.
For instance, the costs of electricity from solar panels has fallen 50% in the last five years. There was a similar drop in the price of rechargeable, lithium-ion batteries for the grid, and estimates indicate that the price will fall another 50% by 2020. This is having an impact on the power generation market. In 2014, nearly 60% of all new investments in power generation went to renewable energy sources.
Running existing power generation infrastructure more efficiently is another example. Reducing losses in transmission and distribution ultimately reduces pressure on the grid. It also lowers the amount of investment required to install new power generation capacities.
The last example relates to buildings. Globally, buildings consume about 40% of all primary energy and produce about one third of the total global energy-related CO2 emissions. Siemens optimised Dubai’s WAFI building complex which includes a hotel, a shopping mall and some health and leisure facilities with a state-of-the-art building automation system. This has cut energy consumption by close to 20%.
Urbanisation is one of the major challenges of this century. If we manage it wisely, we will chart the path to further growth and improve quality of life for more people on our planet. Urban planning and the use of intelligent infrastructure technologies are key levers in the fight against climate change.
Written by Roland Busch, Member of the Managing Board, Siemens AG
This article was also published on the Future of Construction Knowledge Sharing Platform and the WEF Agenda Blog.
--Future of Construction 09:08, 19 Jun 2017 (BST)
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.