Cash flow in construction
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
In general terms, 'cash flow' is the movement of income into and expenditure out of a business (or other entity) over time. If more money is coming into the business than is going out of it, cash flow is said to be 'positive'. If more money is going out, this is negative cash flow.
In construction, however, the term 'cash flow' typically refers to an analysis of when costs will be incurred and how much they will amount to during the life of a project.
Predicting cash flow is important in order to ensure that an appropriate level of funding is in place and that suitable draw-down facilities are available.
[edit] Client cash flow
Until the main contractor has been appointed, client cash flow projections are likely to be based only on agreed fee payment schedules for consultants and a simple division of the construction cost over the likely construction period (or perhaps an allocation of construction cost over an s-curve distribution). It is only when the main contractor is appointed, a master programme prepared and some form of payment schedule agreed that cash flow projections become reliable.
Cash flow projections may be affected by the need for the early purchase of long-lead time items or by items that the client may wish to purchase that are outside of the main contract (such as furniture or equipment).
[edit] Contractor cash flow
Contractors have to have money coming in to pay suppliers and subcontractors and for the day-to-day running of the business. For example, Carillion's cash flow was very low, leading to their liquidation in January 2018.
At the start of any contract, a payment scheme or table is drawn up and agreed with the client or their quantity surveyor, e.g.: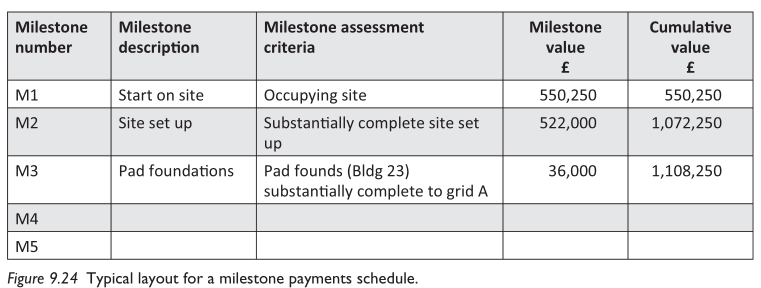
[Brook, M., 2016. Estimating and Tendering for Construction Work. 5th Edition. ed. Taylor & Francis.]
[edit] Supply chain cash flow
Cash flow is also an issue for the construction supply chain, and is a common reason for contractors and sub-contractors becoming insolvent. This can be catastrophic for a project in terms of time and money. It is in the client's interest therefore to ensure that the supply chain is paid promptly.
The government suggest that, 'Historically, it is has not been unusual for lower tier supply chain members to have to wait for up to 100 days to receive payment, which damages their cash flow and can harm their business.' (Ref. Cabinet Office, Project Bank Accounts – Briefing document.)
A number of measures can be adopted to improve payment and so cash flow in the supply chain, including:
In addition, there are a number of remedies for late payment.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Accruals.
- Balance sheet.
- Budget.
- Building society.
- Business administration.
- Cash flow forecast.
- Cash flow statement.
- Commodity.
- Construction supply chain payment charter.
- Credit crunch.
- Demand chain.
- Discounting.
- Discount rate.
- Discounted cash flow.
- Drawdown.
- Earned value.
- Fair payment practices.
- Financial hedging.
- Financial year.
- Microeconomics.
- Net Present Value.
- Payment schedule.
- Profit.
- Project bank accounts.
- Prompt payment.
- Prompt Payment Code boosted to help SMEs.
- Quote.
- Relevant cost.
- Remedies for late payment.
- Retention.
- Solvency.
- Time value of money.
- The Late Payment of Commercial Debts Regulations 2013.
- Trade credit insurance.
- Turnover.
- Whole life costs.
- Working capital.
Featured articles and news
RTPI leader to become new CIOB Chief Executive Officer
Dr Victoria Hills MRTPI, FICE to take over after Caroline Gumble’s departure.
Social and affordable housing, a long term plan for delivery
The “Delivering a Decade of Renewal for Social and Affordable Housing” strategy sets out future path.
A change to adoptive architecture
Effects of global weather warming on architectural detailing, material choice and human interaction.
The proposed publicly owned and backed subsidiary of Homes England, to facilitate new homes.
How big is the problem and what can we do to mitigate the effects?
Overheating guidance and tools for building designers
A number of cool guides to help with the heat.
The UK's Modern Industrial Strategy: A 10 year plan
Previous consultation criticism, current key elements and general support with some persisting reservations.
Building Safety Regulator reforms
New roles, new staff and a new fast track service pave the way for a single construction regulator.
Architectural Technologist CPDs and Communications
CIAT CPD… and how you can do it!
Cooling centres and cool spaces
Managing extreme heat in cities by directing the public to places for heat stress relief and water sources.
Winter gardens: A brief history and warm variations
Extending the season with glass in different forms and terms.
Restoring Great Yarmouth's Winter Gardens
Transforming one of the least sustainable constructions imaginable.
Construction Skills Mission Board launch sector drive
Newly formed government and industry collaboration set strategy for recruiting an additional 100,000 construction workers a year.
New Architects Code comes into effect in September 2025
ARB Architects Code of Conduct and Practice available with ongoing consultation regarding guidance.
Welsh Skills Body (Medr) launches ambitious plan
The new skills body brings together funding and regulation of tertiary education and research for the devolved nation.
Paul Gandy FCIOB announced as next CIOB President
Former Tilbury Douglas CEO takes helm.
UK Infrastructure: A 10 Year Strategy. In brief with reactions
With the National Infrastructure and Service Transformation Authority (NISTA).























Comments
Cash flow is the movement of income into and expenditure out of a business over time. If there is more money going out than in, this is negative cash flow.
Possible cash flow problems may be:
To minimise the risks of future cash flow problems, the firm could establish a financial system that includes: