Bordeaux Law Courts
The design concept involved ‘liberating’ the court-rooms from the ‘box’. The timber-clad solution employs a mix of high technology, computer-controlled machinery and traditional craftsmanship.
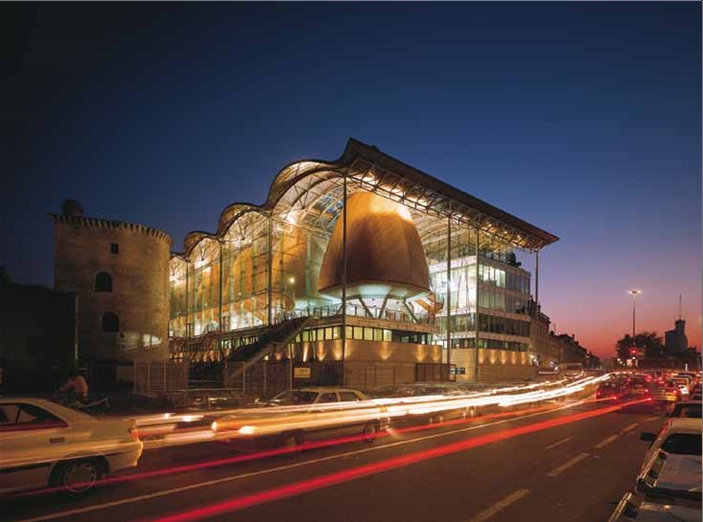
Richard Rogers Partnership (RRP, now Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners, RSH+P) won the international competition to design new law courts for the historic city of Bordeaux in 1992. The design was for a building that would, through a feeling of transparency and openness, create a positive perception of the accessibility of the French judicial system. The brief was complex, requiring complete separation of public and judicial circulation. By pulling the building into its constituent parts, the resulting transparency encourages a sense of orientation, rendering an historically imposing institution more accessible.
Key elements of the design include the creation of public space and integration with the existing urban landscape. Public entry to the building is via a flight of stairs placed to the side, leading to the ‘Salle des Pas Perdus’ at the core of the building, where lawyers, their clients and the public meet.
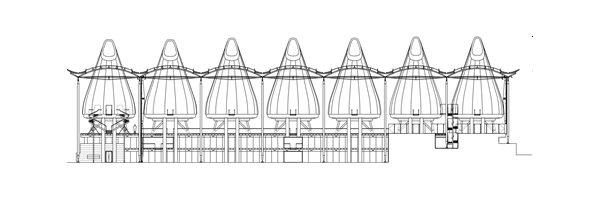
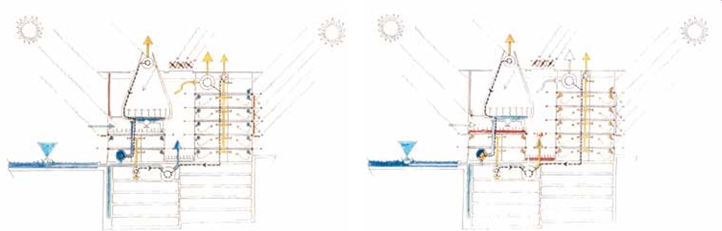
The seven courtroom pods are clad in cedar, raised on pilotis above the limestone plinth within a great glass curtain wall under an undulating copper roof. The administrative offices are reached by bridges spanning the atrium – the clarity of the plan ensuring that different secure routes across the atrium are maintained both for the public and for magistrates. With its use of irregular forms and natural materials, the building successfully complements its sensitive environs, including a section of the city’s medieval wall. A strong emphasis is placed on effective passive control systems. The pods are shaded beneath the great roof and manually-operated brise-soleil windows along the western façade reduce solar gain. The flask-like volumes allow daylight deep into the court rooms and, through their height, ensure temperature control through stratification. The glazed box wrapping around the chambers, with its sun-screening and ventilation systems incorporated within the roof, functions as a breathing container. In addition, the podium and offices are built in concrete – a very effective passive heat control system.
Project information:
- Place / Date: Bordeaux, France 1992—1998
- Client: Tribunal de Grande Instance
- Cost: £27 million
- Gross Internal Area: 25,000m²
- Architect: Richard Rogers Partnership
- Structural Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners/OtH Sud-Ouest
- Services Engineer: OtH Sud-Ouest/Ove Arup & Partners
- Quantity Surveyor: Interfaces, Ingèrop
- Acoustic Consultant: Sound Research Laboratories
- Cladding Consultant: Rice Francis Ritchie
- Landscape Architect: Dan Kiley/Edward Hutchison/Branch Associates
- Lighting Consultant: Lighting Design Partnership
- Main Contractor: Spie Citra Midi Atlantique
- Site Management: OtH Sud-Ouest
Click here to see the full job sheet.
--RSHP
Featured articles and news
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this.