Benefits, not cost, should be focus of key infrastructure projects

|
| The London 2012 Olympics is an example of a major infrastructure project where the benefits to the local area far outweighed the costs. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
More emphasis should be placed on the whole-life benefits of major infrastructure projects rather than cost, says a new ICE policy report. Published in May 2019, the report looks at how the built environment sector can reduce the gap between cost estimates and out-turns for major infrastructure projects.
ICE’s investigation into infrastructure forecasting shows, globally, that it is incredibly difficult to forecast time and cost for major projects due to there being many unforeseen issues that can arise during delivery. Despite these uncertainties, the ultimate measure of success continues to be initial cost forecasts.
The Institution recommendeds that the success measures for projects should shift from an over-focus on costs towards whole-life benefit. The survey data illustrates support from the general public for such a move.
Miles Ashley, Chair of the report’s steering group, said:
“Infrastructure is a vital part of society, with major assets helping to stimulate economic growth, improve health and well-being of the population and protect communities from the effects of extreme weather and climate change.
“We cannot continue to dismiss from the conversation these important benefits. Industry and government need to work smarter, find ways to reduce the disparity between forecasts and out-turns, but also to change the narrative and ensure the wider public, the end users, are also aware of the whole-life benefits these incredible infrastructure projects are bringing to them.”
[edit] Public support
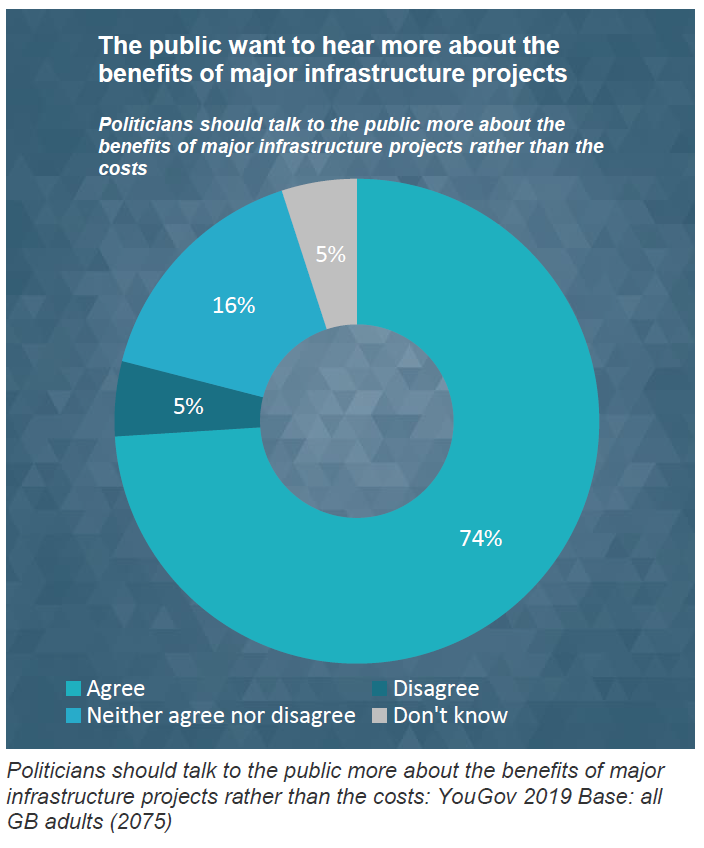
There is public support for the recommendations, with nearly three quarters (74%) of adults agreeing that politicians should talk to the public more about the benefits major infrastructure projects bring, rather than the costs.
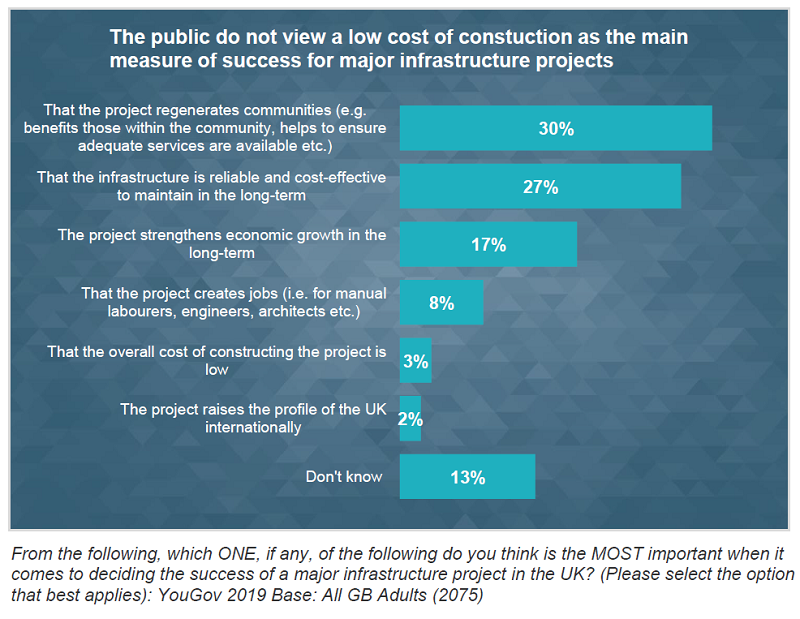
The survey, conducted by YouGov, also found that only 3% of adults feel that a low overall cost of construction should be the most important measure of success of major infrastructure projects.
ICE asked adults across Great Britain what they considered most important in deciding the success of major infrastructure projects:
- 3% said overall cost of construction should be low;
- 17% said the project should strengthen economic growth in the long-term;
- 27% said the infrastructure should be reliable and cost-effective in the long-term;
- 30% said the project should regenerate communities.
Adults were also asked to what extent they agreed that politicians should talk more to the public about the benefits of major infrastructure projects.
- Agree – 74%
- Neither agree nor disagree - 16%
- Disagree – 5%
- Don’t know – 5%
[edit] The recommendations
The report recognises the impact that relying on early estimates, created before full scope and complexity is known, can have on the final 'cost vs out-turn' conversation.
To minimise the disparity between early and final costs, ICE recommends industry adopts the principles set out in the government’s Outsourcing Playbook. It further discusses the way asset owners can use 'should-cost' estimations to obtain fairer and more accurate tenders.
The report also suggests how the Infrastructure Client Group’s Project 13 approach can help the sector move away from transactional arrangements towards an enterprise model.
Chris Richards, ICE Head of Policy and Public Affairs, said:
“Cost and time overruns on major projects is not an issue unique to the UK, it is a global industry challenge. Our paper outlines some of the ways the infrastructure community and government can work together to narrow the gap between cost forecasts and outturn to help alleviate the friction this can cause.
“We can't get away from the fact that major projects by their nature are large, unique and are built over a long time period with many factors that change over that time. The public are alive to that fact, but it is equally important that we continue to highlight the huge benefits these infrastructure projects bring to society.”
The report makes four recommendations:
- Infrastructure owners should complete scope, design and exploration before commencement of work is allowed, to avoid scope creep or retroactive changes, taking steps to include contractors in design at an early stage.
- The government and infrastructure owners must move away from capital cost as the most important metric when assessing project benefits, recognising the importance of whole-life economic, social and environmental value.
- Principles set out in the Outsourcing Playbook should be mandatory for government infrastructure owners, this includes infrastructure owners undertaking 'should-cost' modelling to help inform their expectations and knowledge of appropriate tender prices during the procurement process.
- It should be mandatory for all public infrastructure owners undertaking procurement to award contracts based on a cost estimate range, using a should-cost estimate as a reference point, with an amount of contingency allocated appropriate to the level of project maturity.
ICE will continue to work with government and industry to get these recommendations in practice.
Members with an interest or expertise in this area and who want to get involved through industry conversations or by writing on the ICE Infrastructure Blog should kindly ice.org.uk get in touch.
[edit] About this article
This article was written by Emma Beer of the Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE). It was first published on the ICE website in May 2019 and can be accessed here.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Brexit - The case for infrastructure.
- Government construction and infrastructure pipelines.
- Green infrastructure.
- Growth and Infrastructure Act.
- Infrastructure and Projects Authority.
- Infrastructure UK (IUK).
- Infrastructure nationalisation.
- London infrastructure plan.
- National Infrastructure Pipeline.
- National Infrastructure Plan.
- Nationally Significant Infrastructure Projects.
- Railway engineering.
- Smart cities.
- Traffic and transport.
[edit] Related ICE links
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.