Transitioning to eco-cities: Reducing carbon emissions while improving urban welfare
Author: Susan Roaf
Introduction
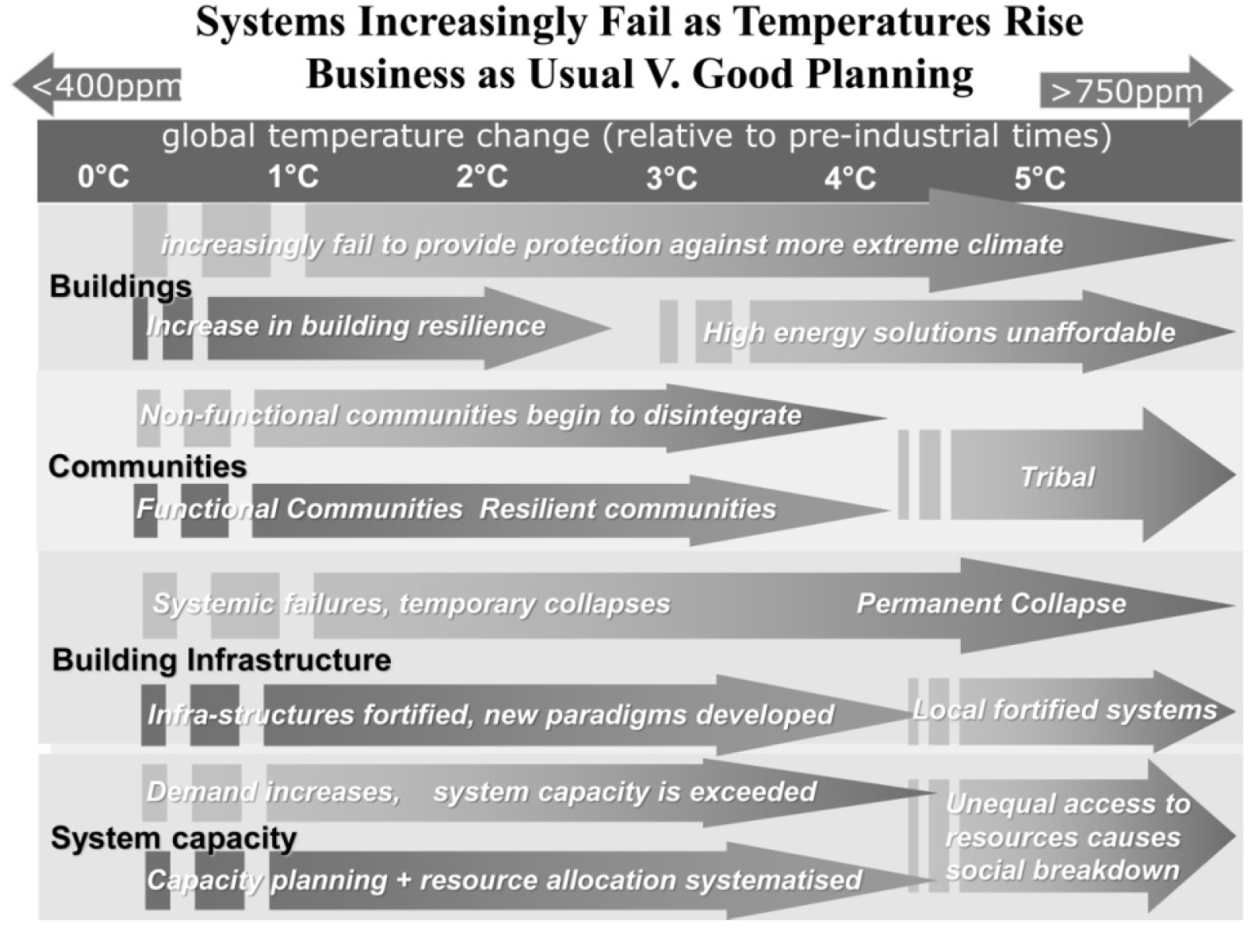
We live in a world where rapid change and unmanaged growth is driving the collapse of established systems, be they top-down macroeconomic failures of the economies such as those of Greece and Spain in 2012, the bottom-up collapse of the housing markets in the United States in 2007–2010, or the escalating failure of infrastructures and buildings to provide adequate shelter during extreme weather events (see Figure 1). While seeking to avoid such collapses, we must understand where economic weaknesses and related breaking points exist and how to measure them. In rapidly evolving systems, we must efficiently draw on experience to grow in successful directions. This chapter tackles the challenges of creating such measures and explores the form they might take, using case studies from Arizona and the city of Dundee in Scotland.
Figure 1: The Warming of the Climate Will Exacerbate the Nature and Rate of Collapse of the Whole Gamut of Our Social and Physical Systems within the Built Environment. Strengthening of These Systems Is Essential to Improve Their Adaptive Capacities and Resilience to Collapse
Source: Roaf et al. 2009.
The chapter is divided into four parts. The first deals with concepts of resilience and adaptive capacity of individuals and populations within that built environment. Part two presents a case study of the failure of the Arizonan housing market in 2007–2010. This details the problem of asymmetric information, the ignorance by the majority of the potentially catastrophic impacts of rising energy, transport and water prices on their own household budgets, and raises the question of how this was allowed to happen in a so-called “responsible” society. Part three introduces the second case study of the city of Dundee in Scotland and a consideration of the role that solar technologies might play in alleviating fuel poverty in that city. The fourth and final part discusses the development of standardised metrics and indicators for describing the adaptive economic capacity of a population and testing the sensitivities of a group to a range of hazards that may threaten to cause the socioeconomic systems within which they operate to collapse. Such metrics and indicators would provide decision makers with the critical ability of testing policies and strategies against the capacity of the system to absorb stress and its breaking points under a range of different conditions. While so doing, such metrics can be used to inform successful adaptation strategies for different populations.
The conclusions clearly point to the social and economic benefits of moving towards facilitating the adoption of wide-scale use of solar energy for domestic populations to reduce economic stress upon them and prevent the collapse of regional housing markets and with them their attendant communities....
This paper was entered into a competition launched by --BRE Group and UBM called to investigate the link between buildings and the wellbeing of those who occupy them.
Related articles on Designing Buildings
- A measure of net well-being that incorporates the effect of housing environmental impacts.
- Adapting 1965-1980 semi-detached dwellings in the UK to reduce summer overheating and the effect of the 2010 Building Regulations.
- Anatomy of low carbon retrofits: evidence from owner-occupied superhomes.
- COP26: A BSRIA summary.
- Energy companies obligation ECO.
- Fuel poverty.
- Green deal scrapped.
- Heat Energy: The Nation’s Forgotten Crisis.
- Housing contribution to regeneration.
- The cold man of europe 2015.
- The real cost of poor housing.
- Well-being and regeneration: Reflections from Carpenters Estate.
- Wellbeing.
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.