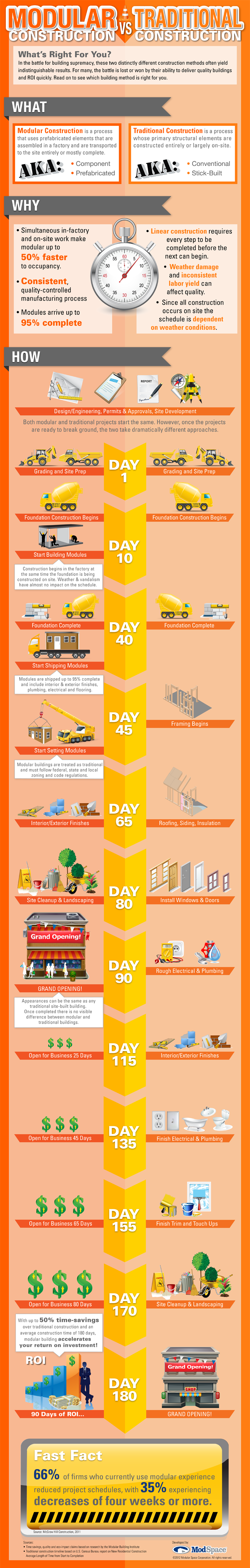
Modular vs traditional construction
This article provides an outline of the important differences between modular and traditional construction methods:
- The term ‘traditional’ is often used to describe the types of linear construction, where each individual step is not only constructed entirely (or largely) on site, but also needs to be completed before the project can move on to the next phase.
- Modular construction is an off-site based construction method, during which individual components are manufactured (or ‘prefabricated’) in a factory, transported to the site entirely (or mostly) complete and assembled on location.
Both construction methods start in the same way – planning, design, approvals, site preparation and development. From that point forward, however, the differences begin:
Image source: Modscape
Pros and Cons of Modular Construction
Pros:
- Thanks to the ability for the project to run simultaneously on-site and in-factory, modular construction can be up to 50% quicker than traditional construction.
- As major parts of construction are handled within a factory, weather conditions are often irrelevant during the majority of the project.
- The factory-based manufacturing process allows not only for greater quality control during the manufacturing process but for many health and safety risks to be considerably reduced, if not eliminated,
- The process aims to minimise waste and reduce the project’s carbon footprint, as fewer people are travelling to the site and modules are produced directly to spec using Computer Aided Manufacturing.
- The impact on the community surrounding the construction site can be significantly reduced, due to much lower levels of noise and traffic during the project period
- The methods employed in modular construction can often benefit the energy efficiency and airtightness of the final construction
Cons:
- Access to the site must be considered from the very beginning, as it will need to allow for the delivery of large modules.
- Traditional construction allows for later design changes, while modular construction is unlikely to be able to factor these in, so early complete design sign off is crucial with clients.
- The logistics and planning of individual module assembly will need rigorous planning to ensure a smooth project.
Ultimately, each project should be considered individually. The method that is selected should match the ultimate desired outcome and the individual limitations of each project.
Featured articles and news
Tackle the decline in Welsh electrical apprenticeships
ECA calls on political parties 100 days to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.






















Comments