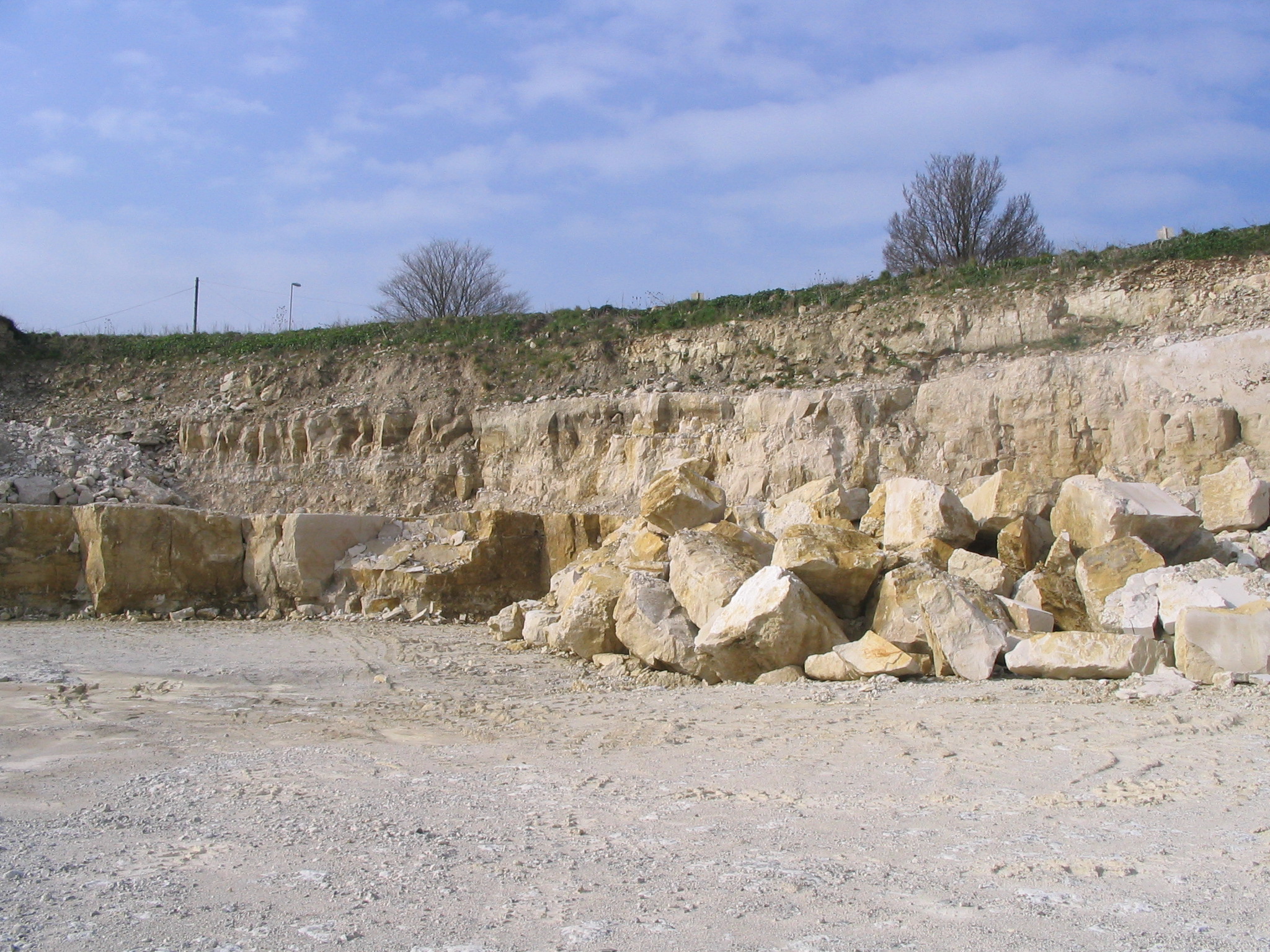
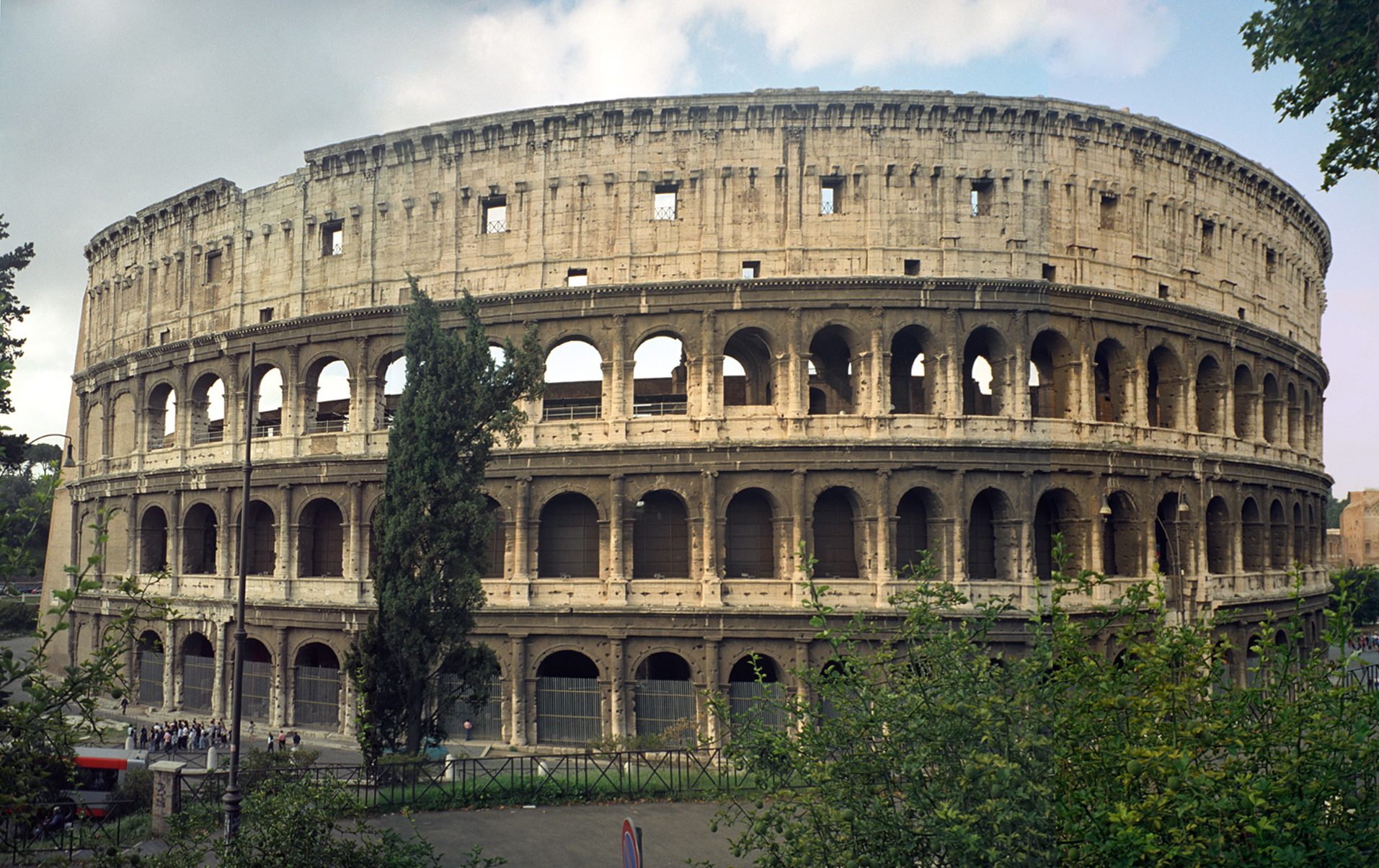
Sustainable stone for the construction industry

|
| A look at stone from the point of view of sustainability, environmental impact and the effect on human health and wellbeing. |
Contents |
[edit] Characteristics of stone
[edit] No embedded carbon
Unlike many other building materials, the quarrying and fabrication of stone releases no embedded carbon, the only greenhouse gases released during quarrying are those used by the fuel to power the quarrying equipment.
[edit] Longevity
Stone is the ultimate long-term building material as the plethora of historical buildings still standing after millennia attests. Used both internally and externally, stone will last for as long as the building with very little maintenance.
[edit] No chemical treatment
Stone does not require treatment with chemicals to render it waterproof and in itself does not pollute or contribute to sick building syndrome, although care must be taken in the choice of fixing materials.
[edit] Recyclable
Stone can be recycled at the end of the building’s life. Building stone is reusable in another building, and any stone fittings that are broken or damaged in removal can be used for mosaics, construction ballast and so on.
[edit] Quarrying stone
To ensure maximum sustainability, specifiers should take care to choose a stone which comes from a plentiful resource rather than a rare or scarce one, and to pick a quarry that is responsibly managed from an environmental point of view as well as a human one.
The Stone Federation has established the Ethical Stone Register, which allows you to verify whether the stone contractor you are using is taking measures to ensure that the stone it buys has been sourced responsibly and ethically.
[edit] Transporting stone
Choosing stones from local quarries minimises the greenhouse gas emissions involved in transporting a heavy material. It also allows you to verify easily that the quarry is responsibly managed. Likewise, the choice of a stonemason close to the installation site ensures that CO2 emissions during transportation of the finished material are minimised.
[edit] Stone fabrication
Select a stonemason that has an environmentally-friendly factory to ensure minimum harm to the environment. The fabrication of finished items from stone involves cutting and in some cases polishing which requires power and water. Modern factories will have taken steps to ensure that the majority of power needs are met by renewable sources and that rainwater harvesting and recycling of greywater makes them self-sufficient, rather than using-up precious resources. Recycling waste material is also a factor that should be taken into account.
[edit] Installing stone
The use of a fabricator close to the site will minimise CO2 emissions during transportation. The method of installation should also use techniques and materials that cause the least possible harm to the environment and to human health.
--Stonecircle 12:38, 03 Sep 2019 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Building with structural stone.
- Choosing stone.
- Defects in stonework.
- Finding stone to conserve historic buildings.
- Inspecting stone sample panels.
- Kentish ragstone.
- Masonry.
- Modern Stonemasonry.
- Natural stone cladding.
- Natural stone for Interiors.
- Natural stone tiles.
- Natural stone.
- Patio stone.
- Penarth Alabaster.
- Portland Stone.
- Sourcing indigenous stone.
- Sourcing stone to repair Exeter Cathedral.
- Stone dressing.
- Two New Ludgate Portland Stone Feature Wall.
- Types of stone.
- Use of Stone in Monks Lantern Weybridge.
[edit] External references
Featured articles and news
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
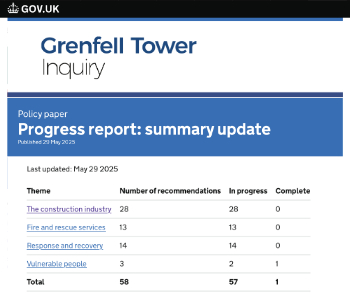
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.
The Remarkable Pinwill Sisters: from ‘lady woodcarvers’ to professionals. Book review.
Skills gap and investment returns on apprenticeships
ECA welcomes new reports from JTL Training and The Electrotechnical Skills Partnership.