Plastic in construction
'Plastic' is a general name given to a wide range of synthetic materials that are based on polymers. The construction industry uses plastic for a wide range of applications because of its versatility, strength-to-weight ratio, durability, corrosion resistance, and so on.
Plastic can be manufactured into forms such as; pipes, cables, coverings, panels, films, sheets and so on; and can be formed or expanded to create low-density materials; and be dissolved in solvents or dispersed as emulsions.
Some of the main types of plastic that are used in construction include:
- Acrylic.
- Composites.
- Expanded polystyrene.
- ETFE.
- Polycarbonate.
- Polyethylene.
- Polypropylene.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- PTFE.
Some of these plastics main uses in the construction industry are:
- Cladding panels.
- Cables.
- Pipes and gutters.
- Windows and doors.
- Shuttering
- Wall linings
- Floor covering
- Ceiling panels.
- Roof coverings.
- Sinks, basins, baths, and showers.
- Worktops
- Insulation materials.
- Membranes.
The advantages of using plastic in construction are that it is lightweight yet strong which makes it easier to transport and shift around sites. It is also resistant to rot and corrosion and has strong weather ability due to it being capable of achieving tight seals. Plastic can also be flexible, and is easily extruded, bent, molded, 3D printed, and so on. Plastic can also be easily removed and some plastics can be recycled.
The disadvantages of plastic are that it has a high embodied energy content and a low modulus of elasticity, meaning that it is generally unsuitable for load-bearing applications. Unless treated, most plastics are also ignitable and have a high thermal expansion rate which requires detailing to allow for adequate thermal movement.
There are environmental concerns about some plastics because of difficulties recycling them, there persistence in the environment after disposal, and concerns regarding chemical additives used to make plastics flexible, resistant to fire, and adhesive.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Adhesives.
- Cladding.
- Construction materials.
- Construction plastics market.
- ETFE.
- Fabric structures.
- Glass reinforced plastic GRP.
- India looks at using plastic instead of sand.
- Nylon.
- Paint.
- Plasticisation.
- Polyethylene.
- Polymers.
- Recyclable construction materials.
- Rubber.
- Sandwich panel.
- Thermoplastic materials in buildings.
- Transparent insulation materials.
- Types of plastic in construction.
- Weatherboarding.
Featured articles and news
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
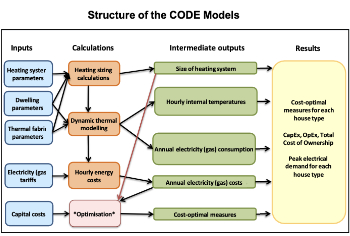
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.






















Comments