Mosaic segmentation
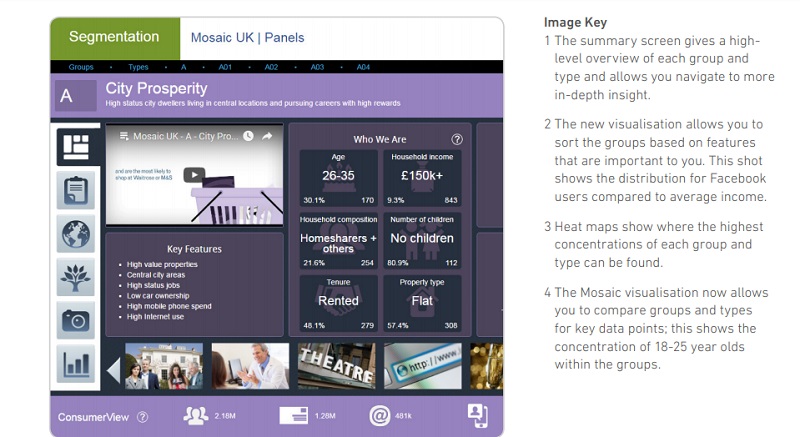
|
| Screen shot of City Prosperity class. Courtesy of Experian. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Mosaic UK is a geodemographic segmentation system devised by marketing services provider Experian to help advance marketing programmes, ensuring that the right information is targeted at the right groups. It is part of a family of Mosaic classifications covering 29 countries including Western Europe, the US, Australia and the Far East.
Mosaic was developed by Richard Webber, a geography professor at Kings College, London, in association with Experian. It is based on the idea that cities globally share common patterns of residential segregation.
[edit] Application
Based on information collected from census, electoral rolls, housing and financial data, Mosaic creates a demographic segmentation which assigns individuals and households into groups and detailed types. This can be used for marketing purposes to target chosen groups with specific information.
Mosaic is said to allow firms to:
- Personalise customer experience to improve retention and share of their spend.
- Understand target audiences and strengthen brand awareness
- Understand new geographic concentrations of customers to optimise location footprint.
Although there are numerous geodemographic segmentation systems, Mosaic is one of the most widely used in the corporate and public sectors, particularly in finance, insurance, retail and telecoms.
[edit] Classification categories
In devising Mosaic, Experian says it identified key demographic changes that influence consumer behaviour. The 2009 version of Mosaic UK has 15 lifestyle (or socio-economic) classifications as follows:
- A – City Prosperity
- B – Prestige Positions
- C – Country Living
- D – Rural Reality
- E – Senior Security
- F – Suburban Stability
- G – Domestic Success
- H – Aspiring Homemakers
- I – Family Basics
- J – Transient Renters
- K – Municipal Tenants
- L – Vintage Value
- M – Modest Traditions
- N – Urban Cohesion
- Q – Rental Hubs
Each of the above classifications is further subdivided, making a total of 66 subclasses. A few examples are as follows:
- A01 – Global high flyers and moneyed families living luxurious lifestyles in London’s most exclusive boroughs.
- C11 – Country-loving families pursuing a rural idyll in comfortable village homes, many commuting some distance to work.
- E21 - Senior singles owning affordable but pleasant homes, whose reduced incomes are satisfactory.
- I39 - Families with children in low-value social houses making limited resources go a long way.
[edit] Mapping
Mosaic data can be overlaid onto maps to highlight the geographic distribution of the chosen parameters and reveal important detail that might otherwise not be discernible. For example, within rural areas, it can highlight households that are likely to be commuting to towns and cities nearby, or residents with more of a local focus i.e in blue collar, agricultural or mining/ manufacturing occupations.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Mixed-use marketing.
- Property marketing.
- Constructing a three year strategic marketing plan.
- Embedding successful key client management.
- Market segmentation.
- Marketing audit.
- One-year tactical or operational marketing plan.
- Routes to market.
- SWOT analysis.
- Winning work.
[edit] External references
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
























