Inverted roof defect - case study
An inverted roof, also referred to as a ‘protected membrane’ or ‘upside down’ roof, is where the waterproofing layer is beneath the thermal insulation layer instead of above it. This means that the temperature within the roof void is closer to that of the building’s interior, without a vapour control layer being required as with a warm roof.
BRE investigated a large building with an inverted roof that was suffering from persistent leaks, with water dripping from the underside of the roof and on to suspended ceiling tiles. When the insulation was removed from the worst-affected area, a large number of water-filled ‘blisters’ were found in the waterproof membrane.
The blisters ranged in size from 50 mm to 1 m and further investigations revealed that they were present across the entire building.
[Figure 1 – Water-filled blisters across roof surface revealed by the removal of the insulation boards]
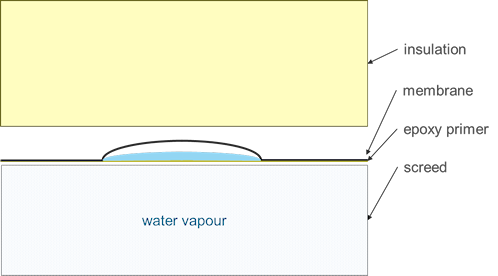
The roof build-up comprised the following elements:
- Ballast.
- Insulation.
- Liquid-applied polyurethane waterproof membrane.
- Epoxy resin primer.
- Concrete screed.
- Pre-cast concrete planks.
The building owners assumed that the blisters had formed because of pinholes and small tears in the membrane, and indeed many such defects were present. However, the majority of the blisters did not contain any defects and there appeared to be no path for water to enter them.
Following an investigation, BRE concluded that water that had been trapped in the roof build-up during construction had condensed between the top of the concrete screed and the underside of the membrane.
The epoxy primer that had been applied to the top of the concrete screed appeared to be acting like a one-way valve, allowing water vapour to pass upwards, but not allowing it to be absorbed back into the screed once it had condensed. This caused the blisters to be ‘pumped up’ with water each time a sudden downpour followed a spell of fine weather.
[Figure 2 – Sketch of condensation within a vapour-filled blister]
It is stressed that this was an unusual occurrence and not one that is normally associated with inverted roofs. Unfortunately the scope of the investigation did not allow BRE to fully investigate the circumstances that had allowed the blisters to form. But the most likely cause was a deficiency in the bond between the liquid-applied waterproof membrane and the primed surface of the concrete screed.
This article was originally published here by BRE.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.