Interferometric synthetic aperture radar InSAR
|
|
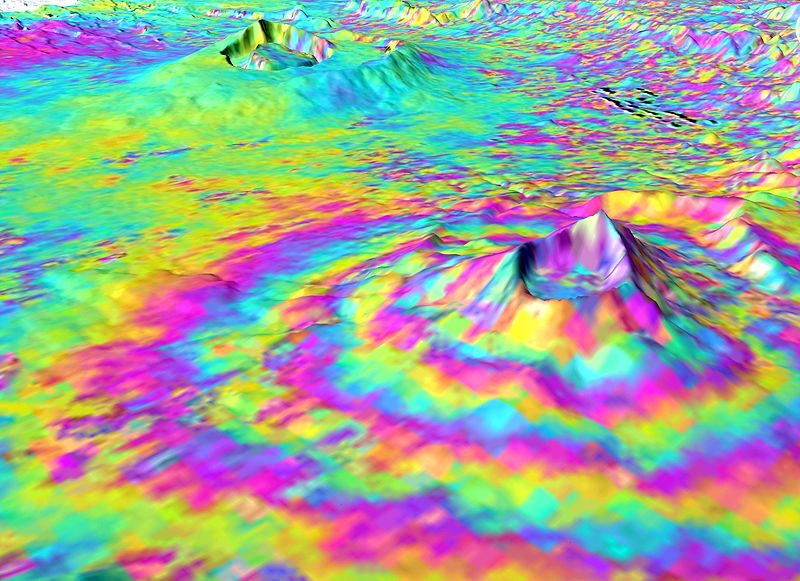
This Envisat Advanced interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) interferogram over the Kenyan section of the Great Rift Valley shows small surface displacements that are not visible to the naked eye of the Longonot volcano (front right). In the background is Suswa volcano, which was not deforming at this time. Using InSAR, a group of scientists discovered that from 1997 to 2000 the volcanoes at Suswa and Menengai (not visible) subsided 2cm to 5cm, and between 2004 and 2006 the Longonot volcano experienced uplift of around 9cm (pictured). Interferogram images appear as rainbow-coloured interference patterns. A complete set of coloured bands, called 'fringes', represents ground movement relative to the spacecraft of half a wavelength, which is 2.8cm in the case of Envisat's InSAR. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (abbreviated as InSAR or IfSAR) is a technique that uses satellite or aircraft radar signals from multiple sources to capture complex and precise measurements.
[edit] Where it can be used
InSAR is a highly effective way to measure changes in land surface altitude. The technique uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images and ‘interferes’ them to interpret differences and produce interferograms. This is an accurate way of detecting ground movements and can be scaled from single pixels (typically 3m x 3m or 4m x 14m) to entire countries.
Radar waves can be transmitted through most weather conditions and do not require daylight.
[edit] Geophysical disaster detection
The deployment of InSAR was first investigated in the 1980s, with additional exploration in the 1990s. One of the earliest practical applications of InSAR came in 1992, when it was used to measure the after effects of an earthquake in California.
Since those early applications, InSAR has been used to record data associated with landslides, volcanoes and other natural occurrences. In these instances, geotechnical engineers use InSAR as a safe, remote sensing technique for assessing and monitoring movement.
[edit] Subsidence
InSAR has proven effective at recording millimetre-scale shifts of land (such as subsidence). Subsidence can be tracked using historic satellite radar data covering previous decades and then monitored throughout the duration of a project and beyond.
InSAR has also been useful in recording the consequences of subsurface mining and natural resource extraction (both current and historic).
[edit] Structural instability
InSAR can also be used to record the stability of infrastructure (including highways, rail, dams and so on) and to monitor buildings. Movements can occur for a multitude of reasons - inadequate design or poor construction of foundations - but it can be difficult to capture the historic data.
NB Earth observation and aerial surveys, RICS professional standard, 6th edition, September 2021, published on 4 January 2022 by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS), defines interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) as: ‘The measurement of the differences in the phases of the waves between two SAR images acquired over the same area at different times.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Construction drones.
- Digital mapping and cartography.
- Earthquake Design Practice for Buildings.
- Engineers and hurricanes.
- Future proofing construction.
- Geophysical survey.
- Global positioning systems and global navigation satellite systems.
- LiDAR.
- Radar.
- Site surveys.
- Subsidence of buildings.
- Synthetic aperture radar.
- Using satellite imagery to monitor movements in megaprojects.
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.

























