High efficiency particulate arrestance HEPA
|
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
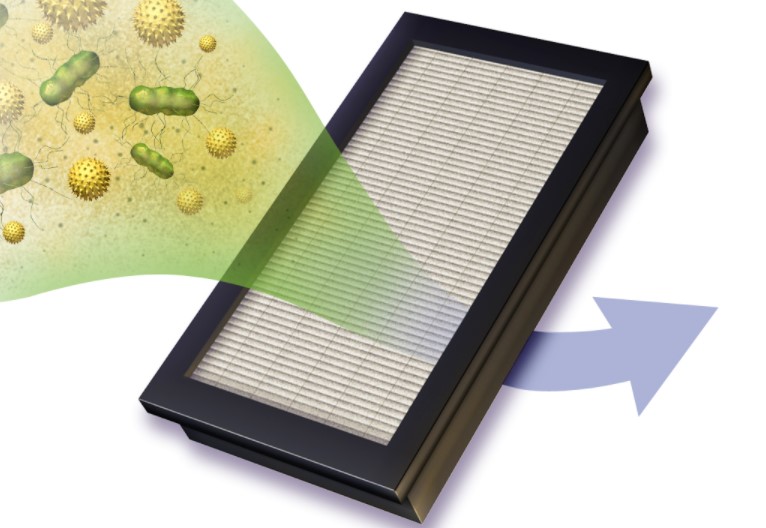
High efficiency particulate arrestance, or HEPA, is a method of air filtration incorporated into a specific type of pleated mechanical particulate absorbing air filter. Due to the mechanical nature of their operations, HEPA purifiers are effective in environments where medical conditions such as asthma or allergies may be prevalent.
[edit] HEPA parameters
To qualify as a HEPA filter, the device must remove 99.95% (EU standard) or 99.97% (ASME, US DOE) of dust, pollen, mould, bacteria and airborne particles with a size of 0.3 microns (µm) from the air that passes through it. However, the term is sometimes used to market products that may not comply with this HEPA standard.
This value is used for filter classification because it is close to the most penetrating particle size (MPPS) of approximately 0.2-0.3 μm (NASA). Particles that are larger or smaller than the MPPS are filtered more efficiently than the rated efficiency, although in some circumstances particles below the MPPS may act as nucleation sites and form particles close to the MPPS.
HEPA filters first became available in the 1950s, but their effectiveness was not technically rated until after the introduction of the minimum efficiency reporting value (MERV) rating system. MERV was developed in the 1980s by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE).
For more information, see Minimum efficiency reporting value MERV.
Using a range from 1 to 20, the MERV rating system reflects the measurement of a filter’s arrestance - or its ability to remove dust from the air - relative to how many of a specific size dust particle (within the range of 0.3 to 10 µm) need to be removed to keep HVAC equipment clean. The higher the MERV rating, the better the filter is at trapping specific types of particles.
In January 2009, ASHRAE stopped recognising general air filters with MERV values based on ratings in the 17 to 20 range. This range is instead represented by HEPA and ultra low particulate air (ULPA) filters, which are capable of removing extremely high levels of dust particles as well as some viruses and other dangerous airborne particulates.
[edit] Proper care and operations of HEPA filters
Appropriate operating conditions are needed in order for HEPA filters to perform as designed. These parameters include velocity and direction of airflow, particle concentration, particle size distribution and appropriate temperature and humidity levels. Design factors, such as non-uniformity of filter pleats or improper filter installation, can also have an impact on the efficiency of these devices.
HEPA filters also need to be inspected and changed on a regular basis. The period between replacement may vary on the setting and the demands of the environment. If the filters are not maintained properly, they will no longer operate efficiently and may even have a negative impact on both the people and the equipment that they are meant to protect.
[edit] HEPA filters and COVID-19
Since COVID-19 is 50 to 200 nanometres in size, it is smaller than the MPPS of HEPA filters, and thus the filter should be able to remove it with at least the rated efficiency.
HEPA filters are not designed to kill viruses and bacteria, which can stay in the filter as long as they survive. This can be up to nine days for COVID-19 in certain conditions. However, COVID-19 survives best on hard surfaces and tends to die faster on soft, porous materials such as filter media.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Air filtration.
- Air filtration and clean indoor air quality standards.
- American Society of Heating and Air-conditioning Engineers.
- Arrestance.
- Building ventilation and COVID-19 transmission risk.
- Clean indoor air for healthy living - New air filter standards.
- Designing HVAC to resist harmful microorganisms.
- Indoor air quality.
- Minimum efficiency reporting value MERV.
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.

























