Water Industry (Scotland) Act 2002

|
| The Scottish Water sewage pumping station, St Andrews. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The Water Industry (Scotland) Act 2002 was passed on 14 February 2002. It is an Act of the Scottish Parliament to "to make further provision in relation to the Water Industry Commissioner for Scotland and to provide for the establishment of Water Customer Consultation Panels; to make further provision in relation to the regulation of the quality of drinking water; to make provision for the establishment of Scottish Water, the transfer to Scottish Water of the functions of the water and sewerage authorities established by section 62(1) of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 and the dissolution of those authorities and in relation to the functions of Scottish Water; to make further amendments of the law relating to water and sewerage; and for connected purposes.'
In England and Wales, requirements for water supply and wastewater services - which were privatised in 1989 - are covered by the Water Industry Act 1991, which came into force in 1991. This was amended by the Water Industry Act 1999, an Act ‘…to make provision in relation to Scotland for the establishment and functions of a Water Industry Commissioner for Scotland’.
[edit] Structure
The Water Industry (Scotland) Act 2002 is split into four parts:
- Part One: Water industry commissioner and the representation of consumers.
- Part Two: Drinking Water Quality Regulator.
- Part Three: Scottish Water.
- Part Four: Miscellaneous and general.
Parts Two and Three of the Act are the most noteworthy in terms of the changes they brought about.
[edit] Part Two: Drinking Water Quality Regulator
The Act established the role of the Drinking Water Quality Regulator (DWQR) - a body which is independent of Scottish Ministers. In addition to ensuring the safety of drinking water in Scotland (primarily by holding Scottish Water accountable), the DWQR handles the monitoring and inspection of the water supply.
Its enforcement powers were established as requirements of The Public Water Supplies (Scotland) Regulations 2014. The DWQR is permitted to act if the requirements of the 2014 regulation are not upheld. It is also able to exercise emergency powers to force water suppliers to carry out actions (such as repairs) if water supplies become compromised.
As part of its efforts to ensure the safety of water supplies, DWQR works with Citizens Advice Scotland. The two entities handle consumer issues that have not been satisfactorily dealt with by Scottish Water.
[edit] Part Three: Scottish Water
The establishment of Scottish Water is perhaps the most significant provision of the Water Industry (Scotland) Act 2002. It replaced the North, South and East of Scotland Water Authorities.
The primary role of Scottish Water is to provide clean water and treat wastewater for homes and businesses in Scotland. It is funded through customer fees and funding allowed by the Water Industry Commission for Scotland.
Despite being a Government entity, Scottish Water has a board structure similar to that of a commercial enterprise, operating under the Water Services etc. (Scotland) Act 2005. The Scottish Government sets the objectives and appoints the chair and non-executive board members of Scottish Water.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Devolution.
- Drinking water quality.
- Drinking Water Quality Regulator for Scotland DWQR.
- Ofwat.
- Pumping station.
- Scottish Government urged to review infrastructure.
- Scottish planning policy.
- The future infrastructure of Scotland.
- Water Act 2014.
- Water for Scotland.
- Water Industry Act 1991.
[edit] External resources
Featured articles and news
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
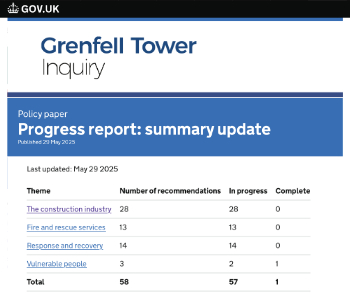
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.
The Remarkable Pinwill Sisters: from ‘lady woodcarvers’ to professionals. Book review.
Skills gap and investment returns on apprenticeships
ECA welcomes new reports from JTL Training and The Electrotechnical Skills Partnership.