Three-layer particle board
Three-layer particle board is essentially a core of larger particle sizes, with increasing density, smaller particle sizes and more resin moving outwards to the edges. This design forms three layers, two with a denser product about a quarter of the depth or less on each side and less dense core with larger chips making up around half of the total thickness. Although the product is described as three layers the three merge into a single mass, though the difference can be seen visually at the sides. It is a heavy weight product and more durable than other particle boards with some external applications.
Standard particle board was originally made in late 19th century Germany, then produced commercially around the Second World War. The earlier board products were often made using blood albumin glue, whilst later commercial products used phenolic resins, amino formaldehyde-, urea formaldehyde-, or urea melamine-based, today there are also particle board products that use glues with lesser environmental impacts. Three-layer particle boards were introduced some time later as a method to reduce the volumes of glue and wood used, whilst retaining most of the same characteristics of a denser board but also increasing weathering capabilities because the external surfaces hace higher resin content.
All particle boards comprise of a small chips and flakes of softwood of varying sizes and density that are impregnated with adhesive (usually amino formaldehyde-, urea formaldehyde-, or urea melamine-based) and subjected to high temperature (up to 220°C) and pressure (2-4MP). When cooled, the boards are cut and sanded, sold either as plain board or faced with laminate. In three-layer particle board the core is first pressed at a lower density, around 600 kg/m3, then the it is sandwiched between two layers of denser particles, around 700-800 kg/m3, containing more binding agent.
Three-layer particle boards can show the same uniformity, as standard particle boards but have the characteristics of denser boards, whilst saving material. The product can be sealed, it is not usually used for external applications but may be suitable for flooring applications.
Normal hand or machine tools can be used for working with three-layer particleboard, it usually take screws similar to denser grades.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Adhesives.
- Blockboard.
- Cedar.
- Chipboard.
- Confederation of Timber Industries.
- Cross-laminated timber.
- Engineered bamboo.
- Glulam.
- Hardboard.
- Laminated veneer lumber LVL.
- Lime wood.
- Low-density fibreboard LDF.
- Medium density fibreboard - MDF.
- Modified wood.
- Oriented strand board.
- Particle board.
- Plywood.
- Single-layer particle board.
- Softwood.
- Timber.
- Timber construction for London.
- Timber preservation.
- Timber vs wood.
- Types of timber.
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
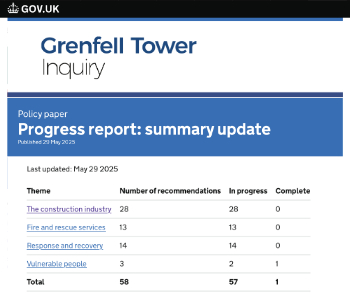
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.