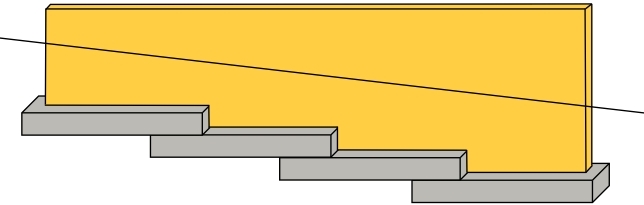
Stepped foundation
Foundations provide support for structures, transferring their load to layers of soil or rock that have sufficient bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
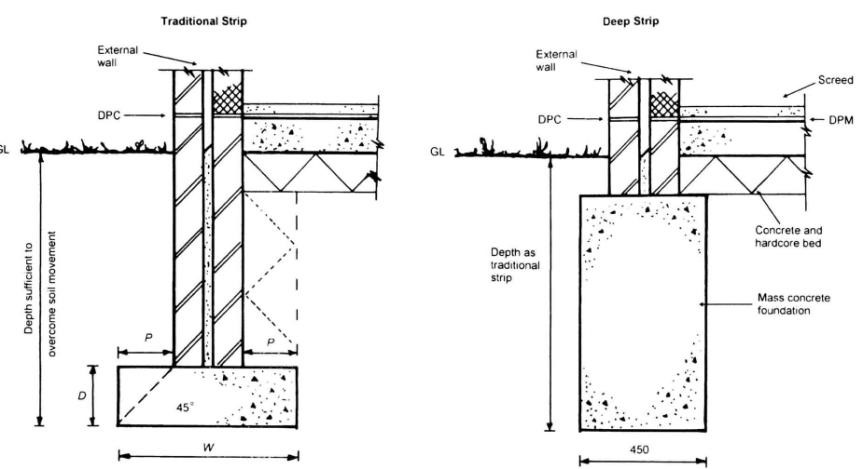
Strip foundations (or strip footings) are a type of shallow foundation used to provide a continuous, level (or sometimes stepped) strip of support to a linear structure such as a wall or closely-spaced rows of columns built centrally above them.
Where the natural surface of the ground is sloped, the most economical solution may be a stepped foundation. In this case, the foundation takes the form of a series of concrete horizontal steps following the slope of the ground.
This helps to minimise the amount of excavation and below-ground wall construction that would otherwise be required. Stepped foundations can also be used to transition from deep foundations to shallow foundations, and at corners and intersections.
Regularly stepping foundations also avoids abrupt and excessive changes in level that could cause a weakness resulting in movement. Similarly, abrupt and excessive changes in foundation depths should be avoided at corners and intersections by the introduction of stepping.
Each step in the foundation should be no higher than the thickness of the foundation. The foundation at the higher level should also overlap the lower foundation, typically by at least twice the height of the step, or by the thickness of the foundation, or by at least 300 mm (whichever is greatest).
Drainage must be carefully designed to eliminate the danger of instability due to accumulating water pressure.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”





















Comments
What are the rebar design standards for stepped footing rebar?
are 90 degree hooks at step down acceptable?