European Court of Human Rights
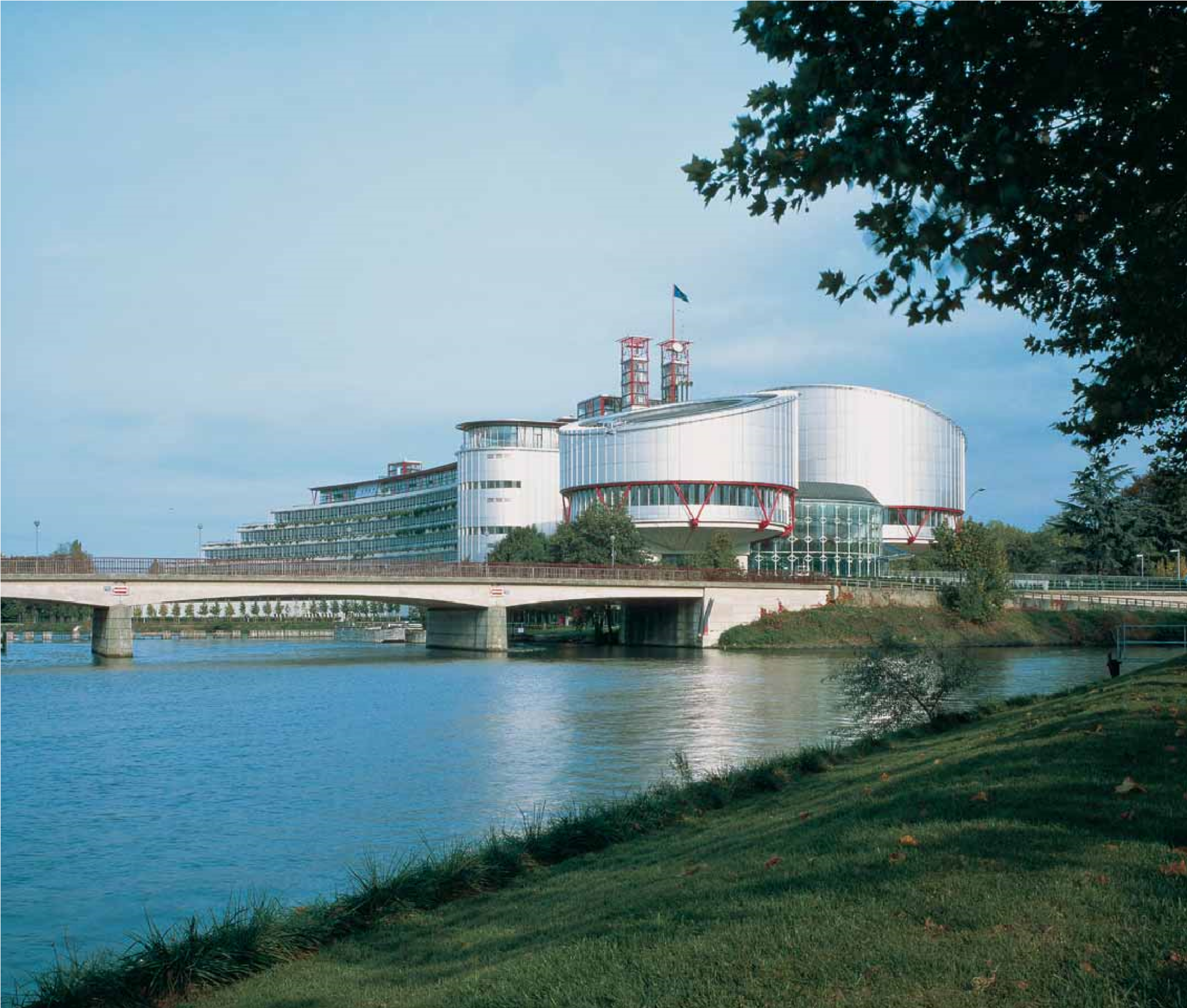
The form of the building, dictated by the sweep of the river Ill, and the work of landscape architect Dan Kiley has resulted in a scheme where building and landscape interact seamlessly.
The European Court of Human Rights is a key building in the history of the Richard Rogers Partnership (RRP, now Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners, RSH+P) and one of the few landmarks which provide a credible architectural image for the new Europe.
The site is located some way from the historic centre of the city but close to the river. The design creates a symbolic landmark but not a monument: the nature of the Court’s business implies that its premises should be anything but intimidating or fortress-like. Rather it should be welcoming and humane, while preserving an appropriate dignity. Protecting and enhancing the quality of the site was a prime objective, along with economy of operation and a ‘natural’ environment.
The basic diagram of the scheme was tested to its limits during the design process. The collapse of the communist bloc greatly increased the European ‘family’: the building’s office provision had to grow by some 50 per cent and the public spaces by 25 per cent.
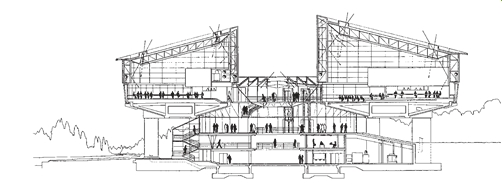
The two main departments of the European Court, the Court itself and the Commission, occupy two circular chambers, clad in stainless steel, at the head of the building, while secondary structural elements are picked out in bright red. The entrance hall is light-filled, and has fine views out over the river. The ‘tail’ of the building is divided into two parts and contains offices, administration and the judge’s chambers. Functions are clearly legible. Only the main public spaces, focusing on a stone-paved rotunda, are air-conditioned (using an economical heat-exchange system). The remainder of the building relies on natural ventilation and light with opening windows.
Façades provide for a high degree of planting: well established greenery spills down from the roofs. The building is a powerful and highly rational expression of the function it serves but is imbued too with a Mendelsohnian streak of romantic expressionism.
Project information:
- Place/Date: Strasbourg , France 1989 - 1995
- Client: Conseil de l’Europe
- Cost: £35 million
- Area: 300,000 m²
- Cost/m²: £117
- Architect: Richard Rogers Partnership
- Structural Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners/Omnium Technique Européen
- Services Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners/Omnium Technique Européen
- Quantity Surveyor: Thorne Wheatley Associates
- Main Contractor: Campenon Bernard SGE
- Lighting Consultant: Lighting Design Partnership
- Landscape Architect: David Jarvis Associates/Dan Kiley
- Co-Architect: Atelier d’Architecture Claude Bucher
- Acoustic Consultant: Sound Research Laboratories
--RSHP
Featured articles and news
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.