Lath and plaster
Lath and plaster is a technique which was used to finish interior walls and ceilings from the early-18th until the early-to-mid-20th century. It was then generally superseded by drywall techniques and plasterboard.
The process involved laths (thin strips of timber) nailed to timber joists or posts and then covered with built-up layers of plaster. Laths typically measure 25 mm x 6 mm, and are positioned about 6 mm apart from each other to allow the plaster to penetrate into the gaps between them.
Typically three coats of plaster would then be applied:
- A ‘render’ layer about 6 mm thick to bond to and fill the gaps between the laths.
- A ‘floating’ layer about 6 mm thick to provide a relatively smooth surface for the third layer.
- A ‘setting’ layer about 3 mm thick to provide a completely smooth finish for decoration.
The first and second layers typically used a 1:3 lime putty to clean, sharp sand mixture. Animal hair was often added to assist with binding. The mixture for the third layer was usually a 3:1 lime putty to fine sand mixture or lime putty on its own.
As time went on, gypsum or cement was added which helped to reduce the setting time between layers.
The advantage of using lath was that it allowed for ornamental or decorative shapes, and could provide sound insulation and fire resistant properties.
However, it was a skilled craft and was a time-consuming activity and so was largely replaced by the use of pre-manufactured plasterboard towards the middle of the 20th century.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
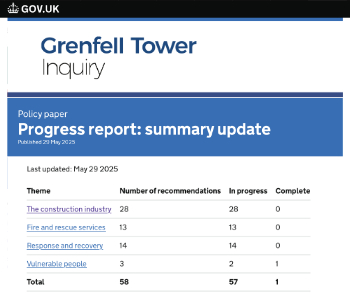
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.
Licensing construction in the UK
As the latest report and proposal to licence builders reaches Parliament.
Building Safety Alliance golden thread guidance
Extensive excel checklist of information with guidance document freely accessible.
Fair Payment Code and other payment initiatives
For fair and late payments, need to work together to add value.
Pre-planning delivery programmes and delay penalties
Proposed for housebuilders in government reform: Speeding Up Build Out.
High street health: converting a building for healthcare uses
The benefits of health centres acting as new anchor sites in the high street.