What is alloy steel?
Alloy steel is a steel that is alloyed with various elements, usually with alloying element content between 1.0% and 50% by weight, in order to improve the mechanical properties of the steel. According to the different alloying elements, alloy steel can be divided into two categories: low alloy steel and high alloy steel. However, there is some controversy about the specific difference between the two. For example, Smith and Hashemi defined the difference as 4.0%, while Degarmo et al. defined it as 8.0%. In most cases, when we refer to the term "alloy steel", we usually mean low alloy steel.
Strictly speaking, every type of steel can be considered an alloy because steel is made by alloying iron with carbon (C) and other elements. However, not all steel is classified as "alloy steel". The simplest steel is alloyed with carbon (C) and iron (Fe), with a carbon content of about 0.1% to 1%, depending on the type of steel. However, when we say "alloy steel", we mean steel that has been deliberately added with other alloying elements in addition to carbon. Common alloying elements include manganese (which is the most common), nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, silicon, and boron. Less common alloying elements include aluminium, cobalt, copper, cerium, niobium, titanium, tungsten, tin, zinc, lead, and zirconium.
Compared to carbon steel, alloy steel has a range of improved properties, including strength, hardness, toughness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, hardenability and thermal hardness. In order to obtain these properties, the metal may need to be heat treated.
Some of these alloys have excellent properties and can be used in particularly demanding applications, such as jet engine turbine blades and nuclear reactors. Due to the ferromagnetic properties of iron, the response of certain steel alloys to magnetism is important in important applications, including applications in electric motors and transformers.
The following are several common low alloy steels:
- D6AC
- 300M
- 256A
see also Types of steel for construction
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
CIOB Apprentice of the Year 2025/26
Construction apprentice from Lincoln Mia Owen wins this years title.
Insulation solutions with less waste for a circular economy
Rob Firman, Technical and Specification Manager, Polyfoam XPS explains.
Recycled waste plastic in construction
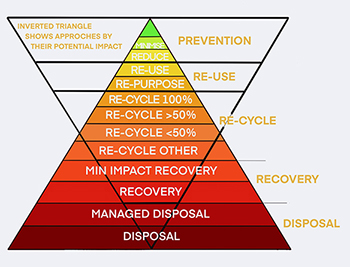
Hierarchy, prevention to disposal, plastic types and approaches.
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.