Quality tools: fishbone diagram
Contents |
[edit] What is it?
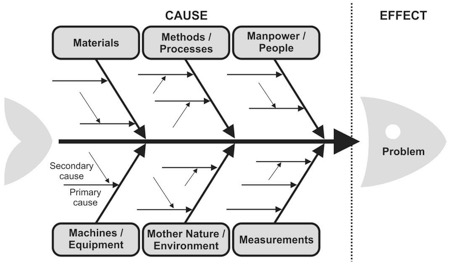
Created by Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, the Fishbone diagram (cause and effect diagram) is a visual tool that shows the potential relationship between a topic (output – effect) and the various factors (inputs – causes) related to it. The diagram resembles the skeleton of a fish as the main causal categories are drawn as ‘bones’ attached to the spine of the fish.
[edit] When and how can I use it?
This tool encourages team participation and is useful in brainstorming. It can be used any time when the cause of a problem is unknown, such as a product defect or issues in the manufacturing or management process. The problem statement and potential categories of causes allow multiple categories of causes to be explored. It can be used as a planning tool to assure that all inputs necessary for a desired outcome have been identified. It can also be used to consider what went right and why during a ‘lessons learned’ exercise at the end of a project.
[edit] Steps
To show the relationships between the cause and effect, and to form a hierarchy of events, the potential causes are arranged based on their level of detail. These are the typical main categories: materials, equipment, people, environment, methods (MEPEM) and sometimes measurement. Facilities, technologies, policies, and practices could be other categories to consider.
1 On the far right side of the diagram write the problem statement. This may be the actual problem or it may be a symptom – at this point you’re not exactly sure and the effect may be refined as more information emerges.
2 Draw a long horizontal arrow pointing to the box. This arrow will serve as the backbone from which further major and minor causes will be categorised and related.
3 Identify potential causes and group them into major categories along the ‘bones’ of the fishbone diagram. Major categories can be established using brainstorming. At this point you shouldn’t be concerned if there is disagreement about whether a category holds the potential cause or not. Just include all of them. Make sure to leave enough space between the major categories on the diagram so that you can add the minor detailed causes.
4 Once you and your team have listed all possible causes you then have the information needed to identify and agree the most likely causes and decide which to investigate further.
[edit] Did you know?
The Fishbone diagram is one of the seven basic quality tools. The Project Management Institute references these seven tools in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge as an example of a set of general tools useful for planning or controlling project quality.
This article was produced by Jo Dovey and Brian Rutter on behalf of the Chartered Quality Institute and published in Quality World, January 2019.
--ConSIG CWG 18:24, 26 May 2019 (BST)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.