Pareto analysis in construction
Pareto analysis is a statistical decision-making technique that identifies a limited number of input factors as having a greater impact on outcomes, whether they are positive or negative. It is based on the Pareto Principle, popularly known as the ‘80/20 rule’, that stipulates that 80% of the outputs result from 20% of the inputs.
The principle was developed by Vilfredo Pareto, a 19th century Italian economist and sociologist who was researching wealth distribution. He subsequently discovered the 80/20 rule applied to areas outside of economics, for example, 80% of the peas in his garden were produced by only 20% of the peapods planted.
Pareto analysis can also be used as a project management tool. For example, the majority of problems (80%) are produced by relatively few causes (20%); and 80% of the project’s benefits are delivered through 20% of the work.
Put simply, Pareto analysis shows that a disproportionate improvement can be made by ranking the various causes of a problem and allocating resources to tackling those that have the largest impact.
In construction, there may be a problem with the project programme that is the result of a large number of causes. Through observation and the collection of data, it might be determined that there are 8 causes. Pareto analysis may show that 80% of the problems result from the top 2 or 3 causes. The project management team can then plan an appropriate response, targeting resources at those 2 or 3 causes, rather than all 8.
A Pareto diagram (or chart) can be used to present the analysis, helping the project team to focus on the inputs with the greatest impact.
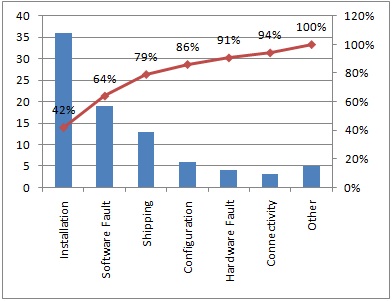
Inputs are listed along the horizontal ‘y’ axis in descending order of output frequency (using the cumulative percentage of the outputs), and uses a line graph to chart them. The vertical ‘x’ axis measures the frequency of the output for each input, and uses a bar graph to chart them.
In the example diagram, it can be seen that 42% of the issues are related to installation, and that three of the categories; installation, software faults, and shipping, account for 79% of the issues.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Acceleration.
- Benchmarking.
- Contingency theory.
- Critical path method.
- Gantt chart.
- Key performance indicators.
- Line of balance (LOB).
- Milestones.
- Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA).
- Project crashing.
- Project manager.
- Project quality plan PQP.
- Quality in construction projects.
- Quality Management System.
- Resource leveling.
- Time-location chart.
- Time management.
- Value management.
- Work breakdown structure
[edit]
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.