Flanges in construction

|
|
[edit] Introduction
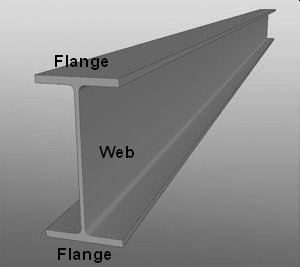
A flange is a projecting ridge, rim, collar or ring on an object such as a column, beam, pipe and so on that provides additional strength or stiffness or additional surface area for the attachment of, or to, another object. For example, flanges may be used to strengthen beams, or to connect or terminate pipes.
Where another object is to be attached, a flange may include bolt holes.
[edit] Pipework flange
Flanges are used in pipework systems for connecting and attaching pipes, valves, pumps, and so on. As an external or internal ridge, or rim, flanges are usually designed to interface sections of pipe and enable easy assembly and disassembly.
Typically, a flange is a forged or thrown ring of stainless steel that is welded or screwed to another component in the system. To create a flanged joint in a pipe system, two connecting pieces with flanges at the end are bolted together, with a seal provided by a gasket between them.
The dimensions of flanges are determined by the size of the pipe as well as the pressure class required for the application. The pressure class ratings that flanges are designed to are typically: 150 lb, 300 lb, 400 lb, 600 lb, 900 lb, 1,500 lb, and 2,500 lb. There are many different flange standards worldwide, with organisations such as ASME, MSS, and API publishing standards.
There are numerous types of flanges, including:
- Blind: This is a plate for covering or closing the end of a pipe, mainly used as part of high pressure weight applications.
- Expander: The non-flanged end is larger than the flanged end. This is used to change the size of a pipe run.
- Groove/tongue: This combination of a raised ring (tongue) and depression (groove) align together precisely.
- High hub blind: This is a simple round plate without a centre hold.
- Lapped joint: Used on applications with lap joint stub ends or lapped pipes, typically where cleaning or inspection is regularly required.
- Orifice: Typically used with orifice metering systems for gauging liquid and gas flow rates.
- Plate: Similar to a gasket, typically used in applications made from casting.
- Reducing: Used in applications with different pipe diameters.
- Ring type joint: A metal ring with a hexagonal groove compressed to a flange to form a seal.
- Slip-on: This flange slips over the pipe and is welded at the top and base side.
- Socket weld: Pipes are inserted into the sockets of flanges and welded for smooth flow. This tends to be used for smaller pipes.
- Spectacle: Comprises two discs attached with the help of a small metal (usually stainless steel, alloy steel, etc.) section.
- Square: A square-shaped flange.
- Threaded: This flange is fixed to a pipe using threads rather than welding, and so are more commonly used for low pressure applications.
- Weld neck: This helps transfer stress from flange to pipe, and is suitable for high pressure applications.
- Weldo/Nipo: A combination of weld neck flange and a nipolet (a one-piece fitting for valve take-offs, drains and vents).
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.























