Delivering Sustainable Buildings: Savings and Payback - Office Case Study for BREEAM UK New Construction 2014
While the multitude of benefits associated with investing in sustainable development practices are increasingly being recognised, for all new construction projects there is always a bottom line impact to consider.
It is for this reason that, in December 2017, a report exploring the cost implications of achieving BREEAM Very Good and Excellent assessment ratings has been undertaken and published.
The latest BREEAM Briefing Paper, titled 'Delivering Sustainable Buildings: Savings and Payback – Office Case Study for BREEAM UK New Construction 2014', uses a speculative office building project that was the basis of a similar report three years ago to review the costs of sustainability today.
The new work takes account of several factors including the increased energy performance demands of Building Regulations Part L2A and the updated assessment criteria of BREEAM UK New Construction 2014. It also examines the difference between BREEAM uplift costs for a building meeting London Plan energy requirements and the same building not so constrained.
The report is published by researchers at BREEAM and Currie & Brown, the leading international asset management and cost consultancy.
Gavin Dunn, Director at BRE, said:
“This Briefing Paper gives developers an updated picture of the cost implications of sustainable development. Both capital and lifecycle costs are considered. In particular, lifecycle costs are examined in respect of energy strategies, and water consumption, including different water supply tariffs.”
The report found that the cost uplift of achieving BREEAM UK New Construction 2014 Excellent ratings is typically less than one per cent of the total construction cost. Analysis of additional costs associated with BREEAM certification at a high standard in terms of energy efficiency and water saving technologies also showed that these costs are relatively modest and that forecast paybacks are quick – typically less than five years for energy and less than two years for water.
Adam Mactavish, operations director at Currie & Brown, points out: “Achieving a high rating under BREEAM 2014 can incur additional costs, but these are less than 1% of the total construction cost. Moreover, long-term savings on energy and water are substantial.”
The challenge for developers and clients is to make sure they consider these issues at an early stage in the design process to secure the benefits and take advantage of a building’s potential to deliver high performance standards by operating them efficiently.
To download a copy of this report see here.
This article was originally published here by BRE Buzz on 17th Dec 2017. It was written by Simon Guy.
--BRE Buzz
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Architects, architecture, buildings, and inspiration in film
The close ties between makers and the movies, with our long list of suggested viewing.
SELECT three-point plan for action issued to MSPs
Call for Scottish regulation, green skills and recognition of electrotechnical industry as part of a manifesto for Scottish Parliamentary elections.
UCEM becomes the University of the Built Environment
Major milestone in its 106-year history, follows recent merger with London School of Architecture (LSE).
Professional practical experience for Architects in training
The long process to transform the nature of education and professional practical experience in the Architecture profession following recent reports.
A people-first approach to retrofit
Moving away from the destructive paradigm of fabric-first.
International Electrician Day, 10 June 2025
Celebrating the role of electrical engineers from André-Marie Amperè, today and for the future.
New guide for clients launched at Houses of Parliament
'There has never been a more important time for clients to step up and ...ask the right questions'
The impact of recycled slate tiles
Innovation across the decades.
EPC changes for existing buildings
Changes and their context as the new RdSAP methodology comes into use from 15 June.
Skills England publishes Sector skills needs assessments
Priority areas relating to the built environment highlighted and described in brief.
BSRIA HVAC Market Watch - May 2025 Edition
Heat Pump Market Outlook: Policy, Performance & Refrigerant Trends for 2025–2028.
Committing to EDI in construction with CIOB
Built Environment professional bodies deepen commitment to EDI with two new signatories: CIAT and CICES.
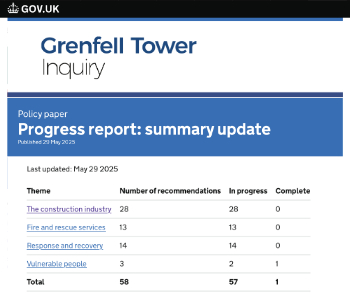
Government Grenfell progress report at a glance
Line by line recomendation overview, with links to more details.
An engaging and lively review of his professional life.
Sustainable heating for listed buildings
A problem that needs to be approached intelligently.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Deadline for entries has been extended to Friday 27 June, so don't miss out!
CIAT at the London Festival of Architecture
Designing for Everyone: Breaking Barriers in Inclusive Architecture.
Mixed reactions to apprenticeship and skills reform 2025
A 'welcome shift' for some and a 'backwards step' for others.